Discover how acupuncture can be a powerful and natural treatment option for infertility.
The Role of Acupuncture in Treating Infertility
Infertility can be a challenging and emotional journey for many couples hoping to start a family. Thankfully, advancements in medical treatments and alternative therapies have provided new hope for those struggling with this issue. One such alternative therapy that has gained popularity in recent years is acupuncture. This ancient practice originating from China is believed to have numerous health benefits, including the potential to improve fertility. In this article, we will explore the role of acupuncture in treating infertility, delving into the causes and treatments of infertility, the basics of acupuncture, the connection between acupuncture and infertility, the acupuncture treatment process for infertility, as well as the risks and considerations associated with this therapy.
Understanding Infertility: Causes and Treatments
Infertility affects millions of couples worldwide, and its causes can be diverse and multifactorial. From physiological issues such as hormonal imbalances, irregular ovulation, or structural abnormalities, to lifestyle factors such as stress, poor nutrition, and exposure to toxins, the origins of infertility can vary greatly from person to person. However, thanks to advancements in medical science, there are now various treatments available to address these underlying causes and increase the chances of conception.
When it comes to understanding infertility, it is important to explore the common causes that can contribute to this condition. These causes can range from endocrine disorders like polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders, to structural issues such as blocked fallopian tubes or uterine abnormalities. Male factors, including low sperm count, poor sperm quality, or hormonal imbalances, can also play a significant role in infertility. Additionally, age-related decline in fertility is a common factor that many couples face. In some cases, infertility may be classified as unexplained, where no known cause can be identified despite thorough testing and evaluation.
Traditional Treatments for Infertility
Traditional treatments for infertility have come a long way in helping couples achieve their dream of starting a family. Hormonal therapies, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI), have proven to be effective in increasing the chances of conception. These methods involve carefully monitoring the woman’s menstrual cycle, stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, and retrieving the eggs for fertilization in a laboratory setting. The resulting embryos are then transferred back into the woman’s uterus, where they have the potential to implant and develop into a pregnancy.
In cases where structural abnormalities are identified, surgical interventions may be recommended. These procedures aim to correct any issues that may be hindering the natural process of conception. For example, if a woman has blocked fallopian tubes, a surgical procedure called tubal ligation reversal can be performed to restore fertility. Similarly, if there are uterine abnormalities, such as fibroids or polyps, a surgical procedure called hysteroscopy can be done to remove these growths and improve the chances of successful implantation.
Alternative Therapies for Infertility
While traditional treatments have proven to be successful for many couples, some individuals may seek alternative therapies to complement or as an alternative to these methods. One such therapy is acupuncture, an ancient Chinese practice that involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body.
Acupuncture is believed to help regulate the body’s energy flow, known as Qi, and promote overall well-being. In the context of infertility, acupuncture is thought to improve blood flow to the reproductive organs, balance hormones, reduce stress, and enhance the chances of conception. Many couples have reported positive experiences with acupuncture, citing increased relaxation, reduced anxiety, and improved reproductive health.
It is important to note that while acupuncture may be beneficial for some individuals, it is not a guaranteed solution for infertility. Each person’s journey is unique, and what works for one couple may not work for another. It is always recommended to consult with a qualified healthcare professional who specializes in fertility to discuss the best treatment options for your specific situation.
The Basics of Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a key component of traditional Chinese medicine. Dating back thousands of years, this ancient practice is based on the belief that the body’s energy, known as Qi (pronounced “chee”), flows through pathways called meridians. When the flow of Qi is disrupted or imbalanced, it can lead to various health issues, including infertility. Acupuncture aims to restore the balance and harmonize the body’s energy.
Acupuncture is not just about inserting needles into the body; it is a holistic approach to healing. Practitioners of acupuncture take into account the patient’s overall health, lifestyle, and emotional well-being. They believe that the body is interconnected, and by addressing the root cause of the imbalance, they can restore harmony and promote healing.
The History and Philosophy of Acupuncture
Acupuncture has a rich history dating back to ancient China. It is believed to have originated around 100 BCE and has since evolved into a widely practiced form of therapy used worldwide. The philosophy behind acupuncture is deeply rooted in the concept of Yin and Yang, the opposing forces that govern the universe and the body. According to traditional Chinese medicine, when Yin and Yang are in balance, the body is healthy. However, when there is an imbalance, illness and disease can occur.
Traditional Chinese medicine views the body as a microcosm of the universe, with the meridians representing the rivers of energy flowing through it. These meridians connect the various acupuncture points, which are like gateways to access and regulate the flow of Qi. By inserting fine needles into specific points along these meridians, acupuncturists aim to restore the natural flow of Qi and promote healing.
Acupuncture is not limited to just physical ailments; it also addresses emotional and mental well-being. Traditional Chinese medicine recognizes the interconnectedness of the mind, body, and spirit. Therefore, acupuncture treatments often include techniques to promote relaxation, reduce stress, and restore emotional balance.
How Acupuncture Works: The Science Behind the Technique
The science behind acupuncture is still being studied, but several theories attempt to explain its mechanisms of action. One theory suggests that acupuncture stimulates the release of endorphins, which are natural pain-relieving chemicals in the body. These endorphins not only help alleviate pain but also promote a sense of well-being and relaxation.
Another theory proposes that acupuncture promotes the release of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, which can help regulate mood and promote overall well-being. Serotonin is known as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter and plays a crucial role in maintaining emotional balance. By stimulating specific acupuncture points, practitioners may be able to influence the release of serotonin and other neurotransmitters, leading to improved mood and mental health.
Research also suggests that acupuncture may impact the autonomic nervous system, which regulates various bodily functions, including reproductive health. By stimulating specific acupuncture points, acupuncturists may be able to influence the autonomic nervous system, promoting better regulation of hormones and enhancing fertility.
While the exact mechanisms of acupuncture are still being explored, its effectiveness in treating a wide range of conditions cannot be denied. From pain management to stress reduction, acupuncture has been embraced by many as a safe and natural form of therapy.
Acupuncture and Infertility: The Connection
The connection between acupuncture and infertility lies in its potential to restore balance and improve overall health and well-being. By targeting specific points along the body’s meridians, acupuncture aims to stimulate the body’s natural healing mechanisms and promote optimal reproductive function.
Acupuncture, an ancient Chinese practice, has gained popularity in recent years as a complementary therapy for infertility. It is believed that acupuncture can address the underlying causes of infertility, such as hormonal imbalances and poor blood circulation, by restoring the body’s energy flow.
When it comes to infertility, hormonal imbalances can disrupt ovulation and menstrual cycles, making it difficult for couples to conceive. Acupuncture is thought to help regulate these imbalances by stimulating the release of certain hormones, such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which are essential for the reproductive process.
Theories Behind Acupuncture’s Effect on Infertility
Several theories attempt to explain how acupuncture may improve fertility. One theory proposes that acupuncture helps regulate hormonal imbalances that can disrupt ovulation and menstrual cycles. By restoring hormonal balance, acupuncture may increase the chances of successful conception. Additionally, acupuncture is believed to improve blood flow to the reproductive organs, including the uterus and ovaries, which can enhance their function and receptivity to fertilization.
Another theory suggests that acupuncture can reduce stress and anxiety, which are known to have a negative impact on fertility. By promoting relaxation and reducing stress levels, acupuncture may create a more favorable environment for conception to occur.
Furthermore, acupuncture is thought to stimulate the release of endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers, which can help alleviate any physical discomfort or tension that may be hindering fertility. By promoting a sense of well-being and relaxation, acupuncture may enhance the overall reproductive health of individuals seeking to conceive.
What Research Says About Acupuncture and Infertility
While the scientific research on acupuncture and infertility is ongoing, several studies have shown promising results. A review of multiple studies found that acupuncture may improve the success rate of IVF and IUI treatments, increase pregnancy rates, and reduce miscarriage rates. However, further research is still needed to fully understand the mechanisms of action and the specific conditions for which acupuncture may be most effective.
In a study published in the journal Fertility and Sterility, researchers found that women who received acupuncture before and after embryo transfer during IVF had a significantly higher pregnancy rate compared to those who did not receive acupuncture. The researchers suggested that acupuncture may improve blood flow to the uterus, reduce inflammation, and enhance the implantation of embryos.
Another study published in the journal Reproductive Biomedicine Online found that acupuncture may increase the pregnancy rate in women undergoing IVF by improving the quality of eggs and embryos. The researchers hypothesized that acupuncture may enhance ovarian function and improve the development of follicles, leading to better reproductive outcomes.
While these studies provide promising evidence, it is important to note that individual responses to acupuncture may vary. Factors such as the duration and frequency of acupuncture sessions, the skill and experience of the acupuncturist, and the specific fertility issues of each individual can all influence the effectiveness of acupuncture as a treatment for infertility.
Overall, acupuncture offers a holistic approach to infertility treatment, addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of reproductive health. By restoring balance and promoting overall well-being, acupuncture may provide a valuable adjunct therapy for couples struggling with infertility.
The Acupuncture Treatment Process for Infertility
The acupuncture treatment process for infertility generally involves several steps, from preparing for the treatment to the actual session itself.
Preparing for Acupuncture Treatment
Prior to starting acupuncture treatment, it is advisable to consult with a qualified acupuncturist who specializes in fertility issues. They will conduct a thorough assessment of your medical history, lifestyle factors, and specific fertility concerns to develop an individualized treatment plan.
What to Expect During an Acupuncture Session
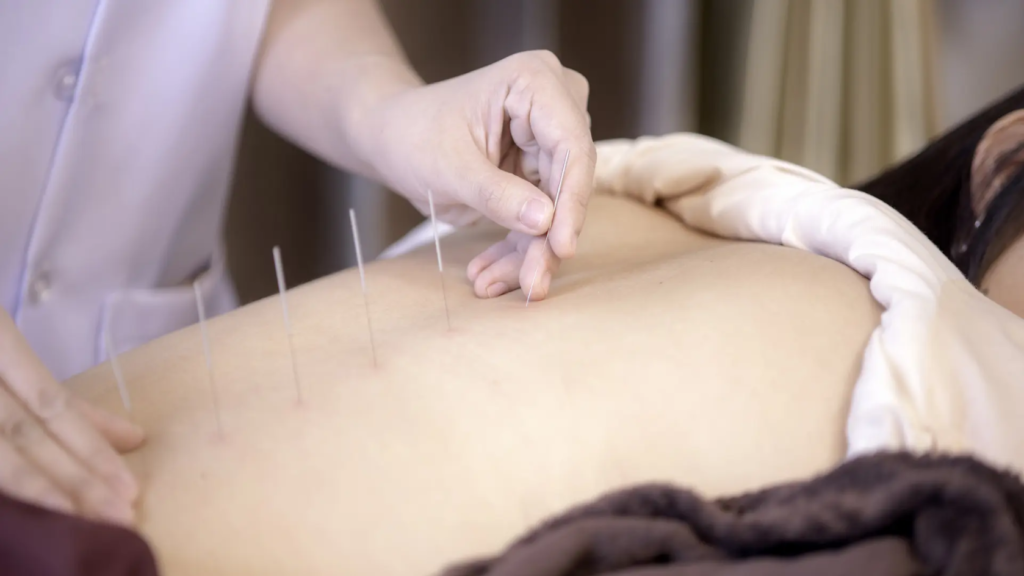
During an acupuncture session, you can expect to lie comfortably on a treatment table while the acupuncturist inserts thin, sterile needles into specific acupuncture points on your body. The needles are generally painless, although you may feel a mild sensation upon insertion. The acupuncturist may also use additional techniques, such as moxibustion (the burning of herbs near the acupuncture points) or electroacupuncture (the application of mild electrical currents to the needles) to enhance the treatment.
Risks and Considerations of Acupuncture for Infertility
While acupuncture is generally considered safe, there are a few risks and considerations to keep in mind when exploring this therapy for infertility.
Potential Side Effects of Acupuncture
Most individuals experience minimal to no side effects from acupuncture. However, it is not uncommon to experience mild bruising or soreness at the needle insertion sites. In rare cases, more serious side effects such as infection or organ injury may occur if the acupuncture is performed by an unqualified practitioner or if proper hygiene practices are not followed.
Who Should Avoid Acupuncture?
While acupuncture is generally safe, some individuals may need to avoid or exercise caution when considering this therapy. Pregnant women should consult with their healthcare provider before beginning acupuncture treatment, as certain acupuncture points may have stimulating effects that could potentially interfere with pregnancy. Additionally, individuals with bleeding disorders or those taking blood-thinning medications should consult with their healthcare provider before undergoing acupuncture, as the procedure may cause bleeding or bruising at the needle insertion sites.
Overall, acupuncture offers a holistic approach to addressing infertility by promoting balance and harmony within the body. While it should not be considered a standalone treatment for fertility issues, it may offer potential benefits when used in conjunction with conventional medical treatments. As always, it is important to consult with qualified healthcare professionals to determine the best course of action for your individual circumstances. With proper guidance and care, acupuncture may play a valuable role in helping couples achieve their dreams of starting a family.