What Causes an Ectopic Pregnancy?

Ectopic pregnancy, a critical medical condition that occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, poses a significant challenge to hopeful parents seeking to expand their families. As fertility rates worldwide shift and assisted reproductive technologies advance, understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options associated with ectopic pregnancies is crucial for both healthcare professionals and prospective parents. This article aims to explore the complex landscape of ectopic pregnancies within the context of fertility, delving into the latest research, preventive measures, and the impact on future reproductive outcomes, offering valuable insights to those navigating the journey towards parenthood.
Table of contents
Understanding Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants itself outside of the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes. This type of pregnancy is non-viable and can lead to severe complications if not treated promptly.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
Several factors may contribute to the development of an ectopic pregnancy:
- Fallopian tube abnormalities: Previous damage or structural abnormalities in the fallopian tubes can make it difficult for the fertilized egg to reach the uterus.
- Inflammation or infection: Pelvic inflammatory disease, often caused by sexually transmitted infections, may lead to scarring and narrowing of the fallopian tubes.
- Previous ectopic pregnancy: A history of ectopic pregnancy increases the risk of recurrence.
- Fertility treatments: Women who have undergone fertility treatments, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), have a higher risk of non-viable pregnancy.
- Contraceptive methods: Although rare, ectopic pregnancy can occur in women using intrauterine devices (IUDs) or following tubal ligation.
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
Early signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy may include:
- Missed period
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Lower abdominal pain
- Dizziness or fainting
- Shoulder pain
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately.
Diagnosing Ectopic Pregnancy
A combination of blood tests, pelvic examination, and imaging studies, such as ultrasound, are used to diagnose ectopic pregnancy by OB/GYN or REI medical specialists. These tests may include:
- hCG blood test: Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone produced during pregnancy. Abnormal hCG levels can indicate a non-viable pregnancy.
- Transvaginal ultrasound: A small probe is inserted into the vagina to create images of the reproductive organs, allowing the physician to locate the pregnancy.
Treatment Options for Ectopic Pregnancy
Extrauterine pregnancies require prompt treatment to avoid complications. Treatment options include:
Medication
If the non-viable pregnancy is detected early and the fallopian tube has not ruptured, a medication called methotrexate may be administered to stop the growth of the pregnancy. Methotrexate comes as a tablet to take by mouth. Your doctor will tell you how often you should take methotrexate. The schedule depends on the condition you have and on how your body responds to the medication.
Surgery
In cases where medication is not an option or if the fallopian tube has ruptured, surgery is necessary to remove the extrauterine pregnancy. Two common surgical approaches are:
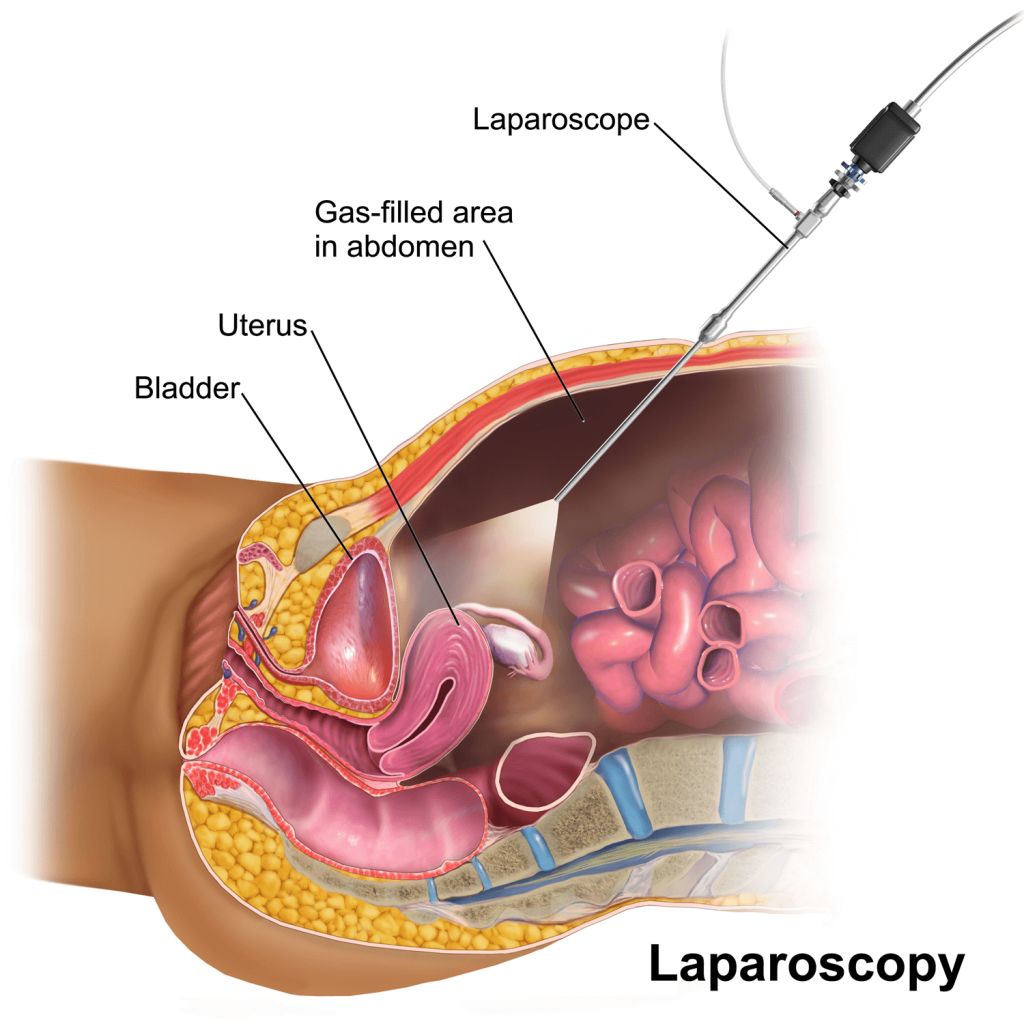
- Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive procedure where a small incision is made in the abdomen, and a thin tube with a camera is inserted to terminate the pregnancy.
- Laparotomy: A more invasive procedure involving a larger incision in the abdomen to remove the ectopic pregnancy, typically performed in emergency situations.
Preventing Ectopic Pregnancy
While not all ectopic pregnancies can be prevented, certain steps can help reduce the risk:
- Practice safe sex to prevent sexually transmitted infections
- Quit smoking, as it can increase the risk of extrauterine pregnancy
- Address any known fallopian tube abnormalities with your healthcare provider
Long-term Outlook and Emotional Support
Experiencing a failed pregnancy, such as an ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage, can be an emotionally challenging and distressing experience. It is essential to seek and receive emotional support during this difficult time to help cope with the loss, manage feelings of grief, and navigate the path to healing. Emotional support can come from various sources, including friends, family, support groups, and professional counselors. Here are some ways to access emotional support and manage emotions after a failed pregnancy:
Open communication: Sharing your feelings and experiences with your partner, friends, or family can help process emotions and provide comfort. Remember that everyone grieves differently, and it is essential to respect each other’s grieving process.
Professional counseling: Seeking the help of a mental health professional, such as a therapist or counselor, can provide valuable guidance and support during this challenging time. They can help you develop coping strategies, manage feelings of grief and loss, and address any concerns about future pregnancies.
Peer support groups: Joining a support group can offer a sense of community and understanding. These groups provide a safe space to share experiences, emotions, and advice with others who have faced similar losses. Many support groups are available both online and in-person, making it easier to find one that fits your needs and preferences.
Self-care
Taking care of your emotional and physical well-being is crucial during the healing process. Engage in activities that bring you comfort and relaxation, such as reading, taking walks, or practicing mindfulness techniques like meditation or yoga. Make sure to get enough sleep, eat a balanced diet, and exercise regularly to support your overall well-being.
Acknowledge your loss: Allow yourself to grieve and acknowledge the loss of your pregnancy. It is essential to give yourself the time and space needed to process your emotions. Recognize that healing is not linear, and it is normal to experience a range of emotions during this time.
Seeking information: Educate yourself about the reasons behind the failed pregnancy and understand the potential risks and outcomes for future pregnancies. Knowledge can provide a sense of control and empowerment, helping you make informed decisions moving forward.
Remember, healing after a failed pregnancy takes time and patience. Each individual’s journey is unique, and there is no specific timeline for recovery. By seeking emotional support and practicing self-care, you can navigate this challenging period and eventually move forward toward healing and planning for future pregnancies.
Frequently Asked Questions About Ectopic Pregnancy
Can an ectopic pregnancy be saved?
Ectopic pregnancies cannot be saved due to the nature of the implantation site. When a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tubes, it is unable to develop into a viable pregnancy. The environment outside the uterus lacks the necessary support structures and nutrients required for the developing embryo. Consequently, the pregnancy cannot progress normally and can pose significant risks to the mother’s health.
The primary concerns with extrauterine pregnancies are the potential for internal bleeding and damage to the reproductive organs. As the embryo grows, it can cause the fallopian tube to rupture, leading to severe pain and life-threatening internal bleeding. This is why immediate medical intervention is crucial when an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed.
What are the chances of having a successful pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy?
The chances of having a successful pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy largely depend on the individual circumstances, the underlying cause of the ectopic pregnancy, and whether any damage occurred to the reproductive organs during treatment. However, many women can go on to have healthy pregnancies following an ectopic pregnancy.
Statistically, the likelihood of conceiving within two years after an non-viable pregnancy is around 60-70%. However, it is essential to note that the risk of experiencing another ectopic pregnancy is slightly increased. Depending on various factors, the risk of a subsequent ectopic pregnancy ranges from 10% to 20%.
Several factors can influence the chances of a successful pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy, including:
The health of the fallopian tubes:
If both fallopian tubes are healthy and undamaged, the chances of a successful pregnancy are higher. However, if one tube is damaged or removed, the likelihood of conceiving may be reduced, but it is still possible to have a healthy pregnancy.
Underlying cause: If the cause of the ectopic pregnancy is a treatable condition, such as pelvic inflammatory disease, treating the underlying issue can improve the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Age: As with all pregnancies, a woman’s age plays a role in fertility. Women over 35 may experience a decreased fertility rate, which could affect the chances of a successful pregnancy following an extrauterine pregnancy.
General health: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, can improve overall fertility and increase the chances of a successful pregnancy.
It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to monitor future pregnancies after a non-viable pregnancy. They can provide guidance on the appropriate waiting period before trying to conceive again and offer personalized advice to maximize the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Can you have a normal pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy?
Yes, many women can have a normal pregnancy after experiencing an extrauterine pregnancy. However, the risk of a subsequent ectopic pregnancy is slightly increased, so it is essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to monitor future pregnancies. It is recommended to consult with a reproductive endocrinologist and infertility specialist (REI)
How long should I wait to try to conceive after an non-viable pregnancy?
It is generally recommended to wait at least three months to allow your body to heal properly. However, your healthcare provider may provide specific guidance based on your individual circumstances.
What is the difference between blighted ovum and an ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy, is a pregnancy that occurs anywhere outside the uterine cavity. A blighted ovum, also known as an anembryonic pregnancy, occurs when a fertilized egg implants in the uterus but fails to develop into an embryo.
Conclusion
In summary, ectopic pregnancies occur when a fertilized egg implants itself outside the uterus, leading to a non-viable pregnancy. Timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications. Although such pregnancies can be distressing, most women can achieve successful pregnancies in the future. By following prevention measures and seeking emotional support, individuals can improve their overall well-being and prepare for future pregnancies.