Uncover all the information that you need to know about a blighted ovum
Blighted Ovum: What You Need to Know
A blighted ovum, also called an anembryonic pregnancy, occurs when a fertilized egg implants in the uterus but fails to develop into an embryo. The placenta and gestational sac may continue to grow, but the absence of an embryo eventually leads to a miscarriage. Anembryonic pregnancies are responsible for approximately 50% of first-trimester or early miscarriages. In this article, we’ll explore the anembryonic pregnancy symptoms, its causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and ways to prevent future anembryonic pregnancy occurrences. We’ll also discuss the emotional impact and the importance of finding support during this difficult time.
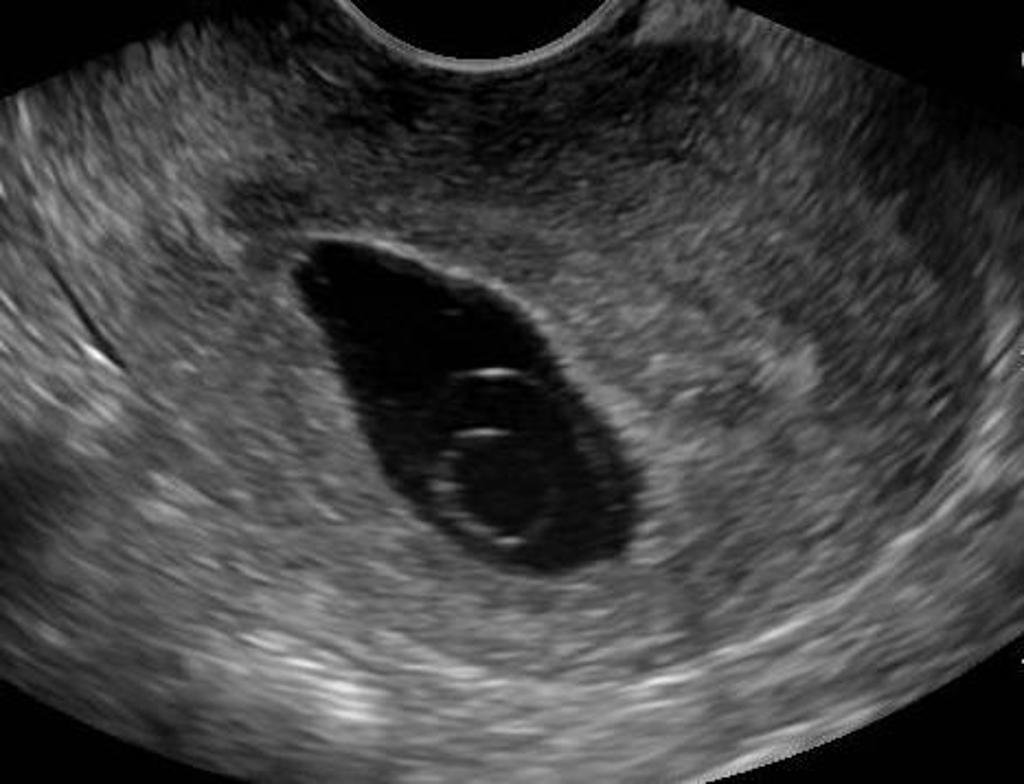

Table of contents
Causes of Anembryonic Pregnancy
Chromosomal Abnormalities
A blighted ovum often occurs as a result of chromosomal abnormalities in the fertilized egg. These abnormalities can occur randomly, and they typically prevent the development of a healthy embryo. In most cases, this is nature’s way of ending a pregnancy that wouldn’t be viable.
Uterine Abnormalities
In some cases, uterine abnormalities can also contribute to a anembryonic pregnancy. These abnormalities may include an irregularly shaped uterus, fibroids, or scar tissue, which can interfere with the proper implantation and development of an embryo.
Anembryonic Pregnancy Symptoms and Diagnosis
Signs of an Anembryonic Pregnancy
An anembryonic pregnancy may initially present with typical pregnancy symptoms, such as missed menstrual period, breast tenderness, and morning sickness. However, as the weeks of pregnancy progresses, some women may experience signs of miscarriage, including vaginal bleeding, abdominal cramping, and a decrease in pregnancy symptoms.
Diagnostic Techniques for Anembryonic Pregnancy
A anembryonic pregnancy is typically diagnosed through an ultrasound examination. During the examination, the doctor will look for an embryo within the gestational sac. If no embryo is present by around six weeks gestation, an anembryonic pregnancy is suspected. Blood tests measuring human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels may also be used to confirm the diagnosis, as hCG levels may be lower than expected or may not rise as they should in a healthy pregnancy.
Treatment Options
Expectant Management
In many cases, a anembryonic pregnancy will naturally result in a miscarriage, and no medical intervention is necessary. This approach, called expectant management, involves waiting for the body to expel the pregnancy tissue on its own. This process can take several weeks, and some women may prefer to discuss other options with their healthcare provider.
Medication for an Anembryonic Pregnancy
If the miscarriage does not occur naturally, medication may be prescribed to help the body expel the pregnancy tissue. Misoprostol is a common medication used in this situation, which causes the uterus to contract and expel the tissue.
Anembryonic Pregnancy Surgical Treatment
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove the pregnancy tissue, especially if there is heavy bleeding or infection. A dilation and curettage (D&C) surgical procedure is typically performed in these cases, where the cervix is dilated, and the tissue is gently scraped or suctioned out of the uterus.
Emotional Impact and Support
Grieving Process
Experiencing anembryonic pregnancy losses can be emotionally devastating for both the woman and her partner. It’s essential to acknowledge the feelings of grief, sadness, and anger that may arise during this time. Everyone’s grieving process is different, and it’s crucial to allow yourself the time and space to heal.
Finding Support
Having a strong support system is essential during this difficult time. Reach out to friends, family, or support groups to share your feelings and experiences. Speaking with a mental health professional or counselor can also provide valuable guidance and coping strategies.
Preventing Future Anembryonic Pregnanies
Prenatal Care
While there is no surefire way to prevent an anembryonic pregnancy, early prenatal care can help identify potential issues in future pregnancies. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor the pregnancy and ensure that the developing baby is healthy.
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can also play a role in promoting a healthy pregnancy. This includes eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, avoiding alcohol and tobacco, and managing stress levels.
Conclusion
A anembryonic pregnancy can be a heartbreaking experience for those who face it. Understanding the causes, blighted ovum symptoms, and treatment options can help couples navigate this difficult time and take steps to ensure a healthy pregnancy in the future. Remember that emotional support is vital during this time, so don’t hesitate to reach out to loved ones or professionals for assistance.
FAQs
1. What is an anembryonic pregnancy?
An anembryonic pregnancy, occurs when a fertilized egg attaches to the uterus but fails to develop into an embryo. This often results in a miscarriage.
2. What causes an anembryonic pregnancy?
Chromosomal abnormalities in the fertilized egg or uterine abnormalities can cause a anembryonic pregnancy.
3. How is an anembryonic pregnancy diagnosed?
A anembryonic pregnancy is typically diagnosed through an ultrasound test and blood tests measuring hCG (The pregnancy hormone) levels.
4. What are the treatment options for an anembryonic pregnancy?
Treatment options for a anembryonic pregnancy include expectant management, medication, or surgical intervention, depending on the individual circumstances.
5. Can I prevent an anembryonic pregnancy in the future?
While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent an anembryonic pregnancy, early prenatal care and adopting a healthy lifestyle can help promote a healthy pregnancy in the future.
6. How long does it take for a miscarriage to occur after an anembryonic pregnancy diagnosis?
The timing of this type of miscarriage after a anembryonic pregnancy diagnosis can vary greatly. In some cases, the body may naturally expel the pregnancy tissue within days or weeks after the initial positive pregnancy test, while in others, it may take longer. It’s essential to discuss your individual situation with your healthcare provider, who can help guide you through the process.
7. Is it possible to have a healthy pregnancy after an anembryonic pregnancy?
Yes, many women who experience a anembryonic pregnancy go on to have healthy pregnancies in the future. An anembryonic pregnancy is often a one-time occurrence due to random chromosomal abnormalities. However, if you have recurrent miscarriages, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to identify any underlying issues.
8. How soon can I try to conceive again after an anembryonic pregnancy?
The optimal time to try to conceive again after an anembryonic pregnancy can vary based on individual circumstances and the specific treatment received. In general, healthcare providers may recommend waiting until after one or two normal menstrual cycles before trying to conceive. It’s crucial to discuss your personal situation with your healthcare provider, who can offer tailored advice.
9. What is the difference between an anembryonic pregnancy and an ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy, is a pregnancy that occurs anywhere outside the uterine cavity. An anembryonic pregnancy, occurs when a fertilized egg implants in the uterus but fails to develop into an embryo.
