Looking to start your journey to parenthood? Discover how to find the best infertility specialist near you.
Find the Best Infertility Specialist Near Me
If you are struggling with infertility and are seeking help, finding the best infertility specialist near you is crucial. Infertility can be a complex and emotionally challenging issue, and the expertise and support of a skilled specialist can make all the difference in your journey towards parenthood.
Understanding Infertility and Its Causes
Before delving into how to find the best infertility specialist, it’s essential to have a basic understanding of infertility and its causes. Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive after one year of trying (or six months if the woman is over 35) without the use of contraceptives. It affects both men and women and can have various underlying causes.
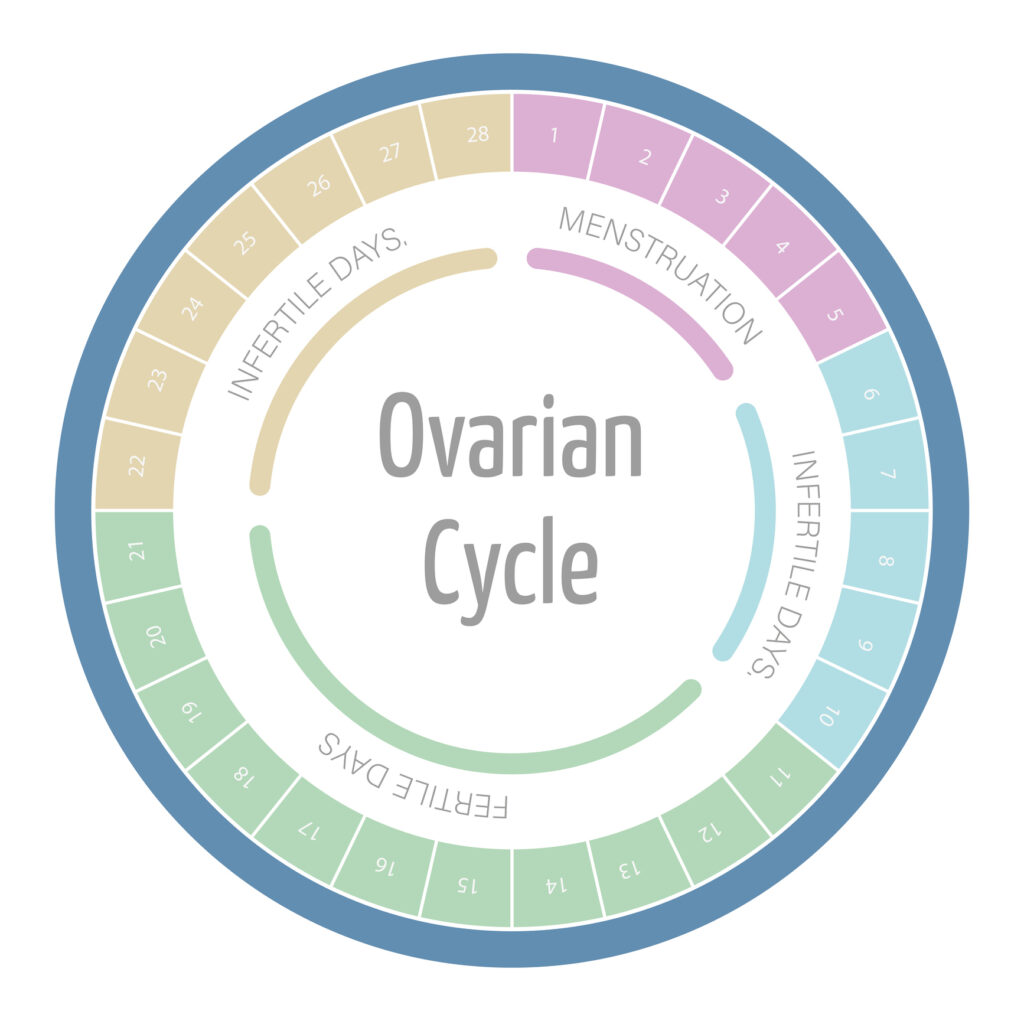
Infertility is a complex issue that can be caused by a multitude of factors. In women, one of the most common causes is ovulation disorders. These disorders can prevent the release of a mature egg from the ovaries, making it difficult for fertilization to occur. Structural issues in the reproductive organs, such as blocked fallopian tubes or uterine abnormalities, can also contribute to infertility in women.
Age-related decline in egg quality is another significant factor in female infertility. As women age, the number and quality of their eggs decrease, making it harder to conceive. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a hormonal disorder that affects the ovaries, can also interfere with a woman’s ability to get pregnant.
On the other hand, male infertility can be caused by various factors as well. One common cause is a low sperm count or poor sperm motility. A low sperm count means that there are fewer sperm available to fertilize an egg, while poor sperm motility refers to sperm that have difficulty swimming towards the egg. Structural abnormalities in the male reproductive system, such as blockages or varicoceles, can also contribute to infertility.
Hormonal imbalances in men can disrupt the production of sperm, leading to infertility. Additionally, genetic disorders or certain medical conditions, such as testicular cancer or diabetes, can affect male fertility.
The Role of an Infertility Specialist

An infertility specialist, also known as a reproductive endocrinologist, is a medical professional who specializes in diagnosing and treating infertility. These specialists have advanced training and expertise in reproductive medicine and offer a range of treatments tailored to individual needs.
When you visit an infertility specialist, they will conduct a thorough evaluation to determine the cause of your infertility. This evaluation may include a review of your medical history, physical examinations, and various diagnostic tests. For women, these tests may include hormone level assessments, ultrasound scans, and hysterosalpingography to check the condition of the fallopian tubes and uterus. Men may undergo semen analysis to assess sperm count, motility, and morphology.
Once the cause of infertility is identified, the infertility specialist will develop a personalized treatment plan. Treatment options may include fertility medications to stimulate ovulation, intrauterine insemination (IUI) to increase the chances of fertilization, or in vitro fertilization (IVF) for more complex cases. In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to correct structural abnormalities or remove blockages.
Throughout the treatment process, the infertility specialist will closely monitor your progress and make adjustments as needed. They will provide guidance and support, addressing any concerns or questions you may have along the way. The ultimate goal is to help you achieve a successful pregnancy and fulfill your dreams of starting a family.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Infertility Specialist
When it comes to selecting the best infertility specialist, several factors warrant consideration. These factors can help ensure that you find a specialist who is the right fit for your needs and preferences.
Qualifications and Experience
One of the first aspects to consider is the qualifications and experience of the infertility specialist. Look for a specialist who is board-certified in reproductive endocrinology and infertility. Their training and experience are vital in providing you with the highest level of care.
An infertility specialist with extensive qualifications and experience can offer a wealth of knowledge and expertise. They have likely encountered a wide range of fertility issues and have developed effective strategies to address them. Their experience can give you confidence in their ability to handle your unique situation.
Furthermore, a specialist who is up-to-date with the latest advancements in reproductive medicine can provide you with access to cutting-edge treatments and techniques. They can offer you the most advanced and effective options available, increasing your chances of success.
Success Rates and Treatment Options
Another crucial factor is the specialist’s success rates and the range of treatment options they offer. Ask about their success rates for treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intrauterine insemination (IUI). High success rates indicate that the specialist has a track record of helping patients achieve their desired outcomes.
Additionally, inquire about their approach to treatment and whether they offer other advanced procedures, such as genetic testing or fertility preservation. A comprehensive range of treatment options can provide you with more choices and increase the likelihood of finding a solution that suits your specific needs.
It is also important to consider the clinic’s approach to personalized care. A specialist who takes the time to understand your individual circumstances and tailors the treatment plan accordingly can provide you with a more personalized and effective experience.
Clinic Location and Accessibility
The location and accessibility of the clinic are also important considerations. Look for a clinic that is conveniently located, with accessible parking and public transportation options. This will make it easier for you to attend appointments and minimize travel-related stress.
Consider the proximity of the clinic to your home or workplace. A clinic that is closer to your daily routine can save you time and make it more convenient to fit appointments into your schedule.
Furthermore, consider the clinic’s hours of operation. A clinic with flexible hours, including evenings and weekends, can accommodate your schedule more effectively.
Finally, consider the overall atmosphere and environment of the clinic. A warm and welcoming clinic can help reduce anxiety and create a more comfortable experience during what can be a challenging time.
The Initial Consultation Process
Once you have identified potential infertility specialists, the next step is to schedule an initial consultation. The initial consultation is an opportunity for you to meet the specialist, share your medical history, and discuss your concerns and goals.
During this crucial first step in your fertility journey, it is important to find a specialist who understands your unique needs and can provide the necessary guidance and support. The initial consultation sets the foundation for your future treatment plan, so it is essential to come prepared and make the most out of this appointment.
What to Expect During Your First Visit
During your first visit, the specialist will likely conduct a thorough evaluation, taking the time to understand your medical history, previous fertility treatments (if any), and any diagnostic tests or procedures you have undergone. This comprehensive assessment allows the specialist to gain a comprehensive understanding of your fertility journey thus far.
In addition to reviewing your medical history, the specialist may also perform a physical examination to assess your overall reproductive health. This examination may include a pelvic exam for women or a semen analysis for men. These tests provide valuable insights into your reproductive health and help the specialist tailor a treatment plan specifically for you.
Furthermore, the specialist may order further tests or screenings to gather more information about your specific situation. These additional tests may include blood work to assess hormone levels, imaging tests to evaluate the structure of your reproductive organs, or genetic testing to identify any underlying genetic factors that may be affecting your fertility.
Preparing for Your Consultation
Before your consultation, it can be helpful to prepare a list of questions to ask the specialist. This could include inquiries about treatment options, success rates, potential risks and side effects, or lifestyle modifications that may improve fertility. By coming prepared with a list of questions, you can ensure that all your concerns are addressed during the consultation.
It is also important to bring any relevant medical records or test results to your consultation. This will provide the specialist with a comprehensive overview of your fertility journey and help them make informed decisions about your treatment plan.
Additionally, it can be beneficial to bring a support person with you to the consultation. Infertility can be an emotionally challenging experience, and having someone by your side can provide comfort and help you remember important details discussed during the appointment.
Remember, the initial consultation is not only an opportunity for the specialist to gather information about your fertility journey but also for you to assess whether the specialist is the right fit for you. Take the time to ask questions, express your concerns, and ensure that you feel comfortable and confident in the specialist’s expertise and approach.
The Emotional Aspects of Infertility Treatment
Infertility and its treatment can take a toll on your emotional well-being. It’s essential to address the emotional aspects along with the physical aspects of treatment.
Infertility can be a challenging and emotionally draining experience. The constant disappointment and longing for a child can lead to feelings of sadness, frustration, and even guilt. It’s important to acknowledge and validate these emotions, as they are a natural response to the difficulties you are facing.
One of the most common emotions experienced during infertility treatment is stress. The pressure to conceive, the uncertainty of the outcome, and the financial burden can all contribute to heightened stress levels. Coping with stress is crucial for your overall well-being. Consider exploring stress management techniques such as meditation, mindfulness, or counseling. These practices can help you relax, reduce anxiety, and regain a sense of control over your emotions.
Furthermore, building a strong support system is vital during your fertility journey. Surrounding yourself with understanding and empathetic individuals can provide immense comfort and encouragement. Seek out support groups or counseling services specifically tailored for individuals and couples dealing with infertility. These resources can offer a safe space to share your experiences, receive validation, and gain coping strategies from others who are going through similar challenges.
Remember that you are not alone in this journey. Many individuals and couples have faced and overcome infertility, and their stories can provide hope and inspiration. Connecting with others who have successfully navigated through infertility can offer reassurance and guidance.
In addition to seeking emotional support, engaging in activities you enjoy can help alleviate emotional distress. Whether it’s pursuing a hobby, exercising, or spending quality time with loved ones, finding moments of joy and relaxation can help you maintain a positive mindset and reduce the impact of infertility on your emotional well-being.
Infertility treatment is a complex and multifaceted process that requires attention to both the physical and emotional aspects. By addressing your emotional well-being and seeking support, you can navigate through this challenging journey with resilience and strength.
Financial Considerations of Infertility Treatment
Infertility treatment can be expensive, and understanding the financial aspects is crucial in making informed decisions.
Understanding Treatment Costs
When researching infertility specialists, inquire about the cost of various treatments and procedures. Some clinics offer bundled or discounted packages, while others have financing options that can help manage the financial burden. Understanding the costs upfront can assist you in planning and budgeting accordingly.
Insurance Coverage and Financing Options
Check with your insurance provider to determine what aspects of infertility treatment are covered. Some insurance plans cover diagnostic testing but may not cover fertility treatments like IVF. Familiarize yourself with your insurance coverage to avoid any surprises. Additionally, inquire about payment plans or financing options that the clinic may offer to make treatment more affordable.
In conclusion, finding the best infertility specialist near you involves consideration of various factors, including qualifications, experience, success rates, and treatment options. It’s also important to prioritize your emotional well-being throughout the process and address the financial aspects of treatment. By taking the time to research and ask the right questions, you can find a specialist who will provide comprehensive care and support on your journey towards parenthood.