Discover your odds of conceiving with the ultimate fertility calculator! This comprehensive tool will help you predict your chances of conception and plan for the future.
The Ultimate Fertility Calculator: Predict Your Chances of Conception
Fertility is a topic that has been surrounded by myths and misconceptions for centuries. Many individuals and couples struggle to understand their chances of conception and find themselves looking for answers. This is where the ultimate fertility calculator comes into play, providing a comprehensive overview of fertility and helping individuals make informed decisions about their reproductive health.
Understanding Fertility: A Comprehensive Overview
When it comes to starting a family, understanding fertility is crucial. Fertility refers to the ability to conceive and carry a pregnancy to term. It is a complex process influenced by various factors, such as age, hormonal balance, and overall health. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of fertility, individuals can make informed decisions and navigate the world of fertility calculators with confidence.
What is Fertility?
Fertility is not just a simple concept; it involves a series of intricate biological processes. In women, fertility begins with the release of an egg from the ovaries, a process known as ovulation. This egg then travels through the fallopian tubes, where it can be fertilized by sperm. If fertilization occurs, the fertilized egg implants itself in the uterus, leading to pregnancy. However, if fertilization does not occur, the uterine lining sheds during menstruation, and the cycle begins anew.
Understanding the basics of fertility is essential for individuals who are trying to conceive. It is important to know that fertility varies from person to person and can be influenced by a range of factors.
Factors Influencing Fertility
Several factors can impact fertility, both positively and negatively. Age plays a significant role in fertility, particularly for women. As women age, their fertility declines due to a decrease in the number and quality of eggs in their ovaries. This decline becomes more pronounced after the age of 35. On the other hand, men also experience a decline in fertility as they age, although it tends to be less drastic.
Hormonal imbalances can also affect fertility. Hormones play a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle and ensuring the proper functioning of the reproductive system. Imbalances in hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, and luteinizing hormone can disrupt ovulation and make it more challenging to conceive.
Underlying medical conditions can also impact fertility. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and uterine fibroids can interfere with ovulation or implantation, making it harder to get pregnant. It is important for individuals with these conditions to seek medical advice and explore appropriate treatment options.
Lifestyle choices can also influence fertility. Factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, and poor nutrition can all have a negative impact on reproductive health. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can help optimize fertility.
Environmental factors can also affect fertility. Exposure to certain chemicals, toxins, and pollutants in the environment can disrupt hormonal balance and impair reproductive function. It is essential to be aware of potential environmental hazards and take necessary precautions to minimize their impact on fertility.
Common Misconceptions about Fertility
There are numerous misconceptions surrounding fertility that can lead to confusion and misinformation. One common myth is that a woman can get pregnant at any point during her menstrual cycle. In reality, a woman is most fertile during her ovulation window, which typically occurs around the middle of her cycle. Ovulation calculators and tracking methods can help individuals identify their most fertile days and increase their chances of conception.

Another misconception is that infertility is always a female issue. In reality, infertility can be caused by factors affecting both men and women. It is important for couples struggling to conceive to seek medical evaluation for both partners to identify any potential underlying causes.
Understanding these misconceptions is vital for accurate fertility calculations. By dispelling myths and gaining accurate knowledge, individuals can make informed decisions and take appropriate steps to optimize their fertility.
The Science Behind Fertility Calculators
Fertility calculators have revolutionized family planning by utilizing advanced algorithms based on scientific research to estimate the likelihood of conception. These algorithms consider a multitude of factors, including menstrual cycle length, ovulation patterns, and other personal information provided by the user. By inputting this data, individuals can receive personalized predictions of their fertile days, empowering them to make informed decisions about their reproductive health.
One of the key elements in fertility calculations is the role of ovulation. Ovulation is a natural process in which a mature egg is released from the ovary, ready to be fertilized by sperm. Fertility calculators take this into account and determine the most fertile days by predicting when ovulation is likely to occur. This knowledge allows individuals to plan intercourse accordingly, increasing the chances of successful conception.
However, it is important to understand the accuracy and limitations of fertility calculators. While they can provide useful insights, several factors can affect their reliability. For instance, women with irregular menstrual cycles may find it challenging to accurately predict ovulation using these calculators. Additionally, underlying health conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or hormonal imbalances, can impact the accuracy of the predictions.
External stressors, both physical and emotional, can also influence fertility. Stress has been shown to disrupt hormonal balance and interfere with ovulation, potentially leading to inaccurate predictions from fertility calculators. Therefore, it is crucial to approach these tools as supportive aids rather than sole determinants of fertility.
When using fertility calculators, it is advisable to consult healthcare professionals for a comprehensive evaluation of your reproductive health. They can provide personalized guidance and address any concerns or questions you may have. Remember, fertility is a complex process influenced by various factors, and seeking professional advice can help you navigate this journey with confidence.
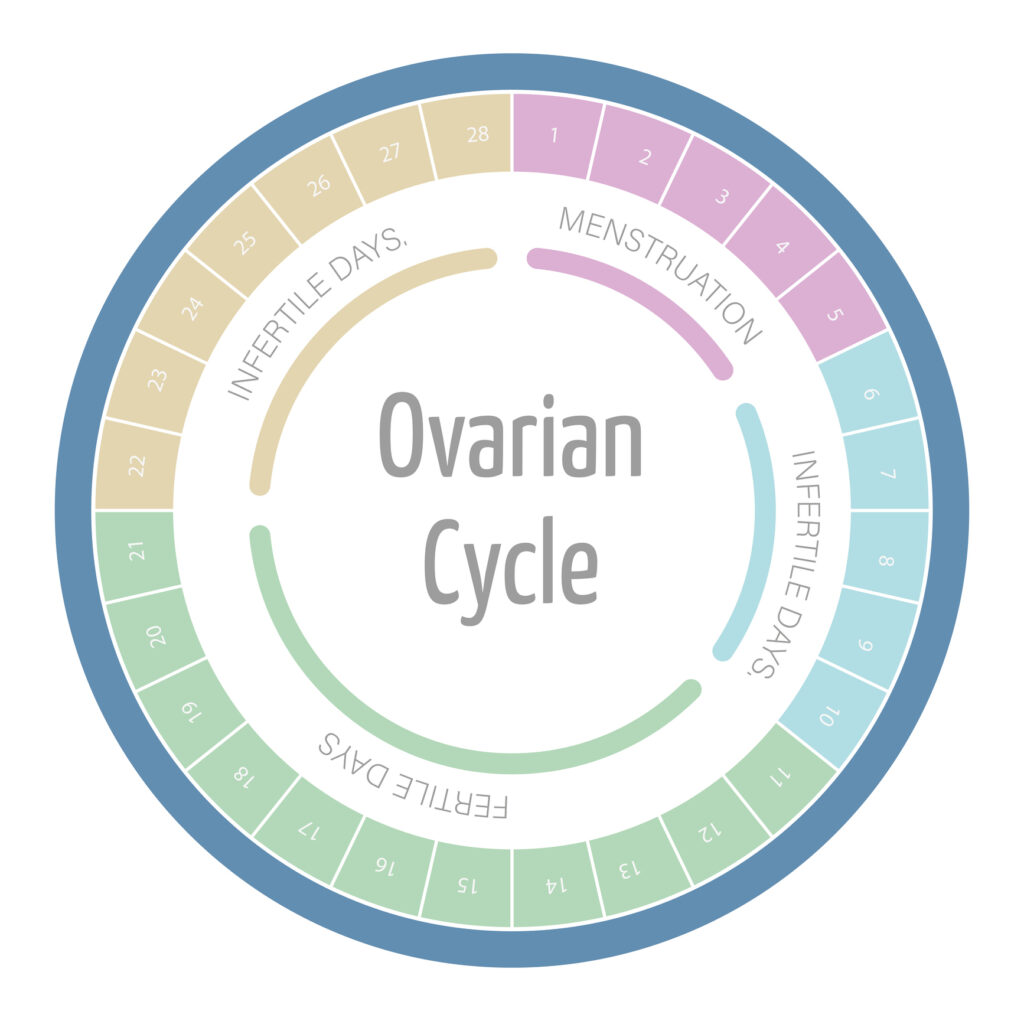
Using the Ultimate Fertility Calculator
Welcome to the ultimate fertility calculator, a powerful tool that can assist you in understanding your fertility and increase your chances of conception. By inputting accurate personal information, interpreting the results, and using the calculator consistently, you can optimize your fertility journey.
Inputting Your Personal Information
Using the ultimate fertility calculator begins with inputting accurate personal information. This includes details about your menstrual cycle length, period duration, and the first day of your last menstrual period. By providing this data, you ensure that the fertility calculator generates more accurate predictions and personalized results.
Accurate information is crucial because it allows the calculator to analyze your unique cycle patterns and predict your fertile days. It is important to be as precise as possible when entering this information to ensure the best possible results.
Interpreting Your Fertility Calculator Results
Once you have entered your personal information, the fertility calculator generates results personalized to your individual cycle. These results often include fertility windows and potential fertile days. It is essential to understand and interpret these results correctly to optimize your chances of conception.
Understanding your fertility windows can help you plan intercourse accordingly, increasing the likelihood of successful conception. The calculator may also provide additional insights, such as the most fertile days within your cycle, which can further enhance your understanding of your fertility patterns.
It is important to note that the fertility calculator provides predictions based on statistical analysis and historical data. While it can be a valuable tool, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance.
Regular Use for Optimal Results
Consistency is key when using fertility calculators. Since menstrual cycles can vary from month to month, regularly updating and tracking your cycle data can improve the accuracy of the results. By using the ultimate fertility calculator consistently, you can identify patterns and gain a deeper understanding of your unique fertility journey.
Regular use of the calculator allows you to track changes in your cycle, identify irregularities, and make informed decisions about timing intercourse. It can also help you monitor the effectiveness of any fertility treatments or interventions you may be undergoing.
Remember, the ultimate fertility calculator is a valuable tool, but it is not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you have concerns about your fertility or are experiencing difficulties conceiving, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized guidance and support.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Fertility
When it comes to fertility, making certain lifestyle changes can have a significant impact on your chances of conceiving. While there are various factors that can affect fertility, including age and underlying medical conditions, focusing on nutrition, exercise, and stress management can optimize your reproductive health. Let’s explore these areas in more detail.
Nutrition and Fertility
A healthy diet plays a vital role in promoting fertility. Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can optimize reproductive health. These foods provide essential nutrients that support the reproductive system and help regulate hormone levels.
One nutrient that has been linked to improved fertility outcomes is folic acid. This B-vitamin is crucial for the development of a healthy baby and can reduce the risk of certain birth defects. Including foods such as leafy green vegetables, citrus fruits, and fortified grains in your diet can help ensure an adequate intake of folic acid.
Omega-3 fatty acids are another nutrient that can positively impact fertility. These healthy fats are found in fatty fish, such as salmon and sardines, as well as flaxseeds and walnuts. Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to improve egg quality and promote a healthy uterine lining, both of which are important for successful conception.
Exercise and Its Impact on Fertility
Regular physical activity has numerous benefits for overall health, including fertility. Engaging in moderate exercise can help regulate hormones, improve blood flow to reproductive organs, and manage stress. Exercise also helps maintain a healthy body weight, which is crucial for fertility.
However, it’s important to strike a balance when it comes to exercise. Excessive exercise, especially high-intensity workouts, can have adverse effects on fertility. Intense exercise can disrupt hormonal balance and interfere with the menstrual cycle, making it more difficult to conceive. Therefore, it’s essential to listen to your body and avoid overexertion.
The Importance of Stress Management
Stress can have a significant impact on fertility. When you’re stressed, your body releases stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can interfere with hormonal balance and menstrual regularity. This can make it harder to conceive.
Incorporating stress management techniques into your daily routine can help reduce stress levels and enhance overall well-being, thus increasing the chances of conception. Activities such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies can help you relax and unwind. It’s important to find what works best for you and make time for self-care.
Additionally, seeking support from loved ones or joining support groups for individuals experiencing fertility challenges can provide emotional support and help alleviate stress.
In conclusion, making lifestyle changes to improve fertility involves focusing on nutrition, exercise, and stress management. By consuming a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, engaging in moderate exercise, and finding effective stress management techniques, you can optimize your reproductive health and increase your chances of conceiving. Remember, every individual is unique, so it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance.
Conclusion
The ultimate fertility calculator is a powerful tool that empowers individuals and couples to understand their chances of conception. By gaining a comprehensive overview of fertility fundamentals, the science behind fertility calculators, and utilizing lifestyle changes to improve fertility, individuals can embark on their fertility journey with confidence and informed decision-making.