Discover expert-backed tips and lifestyle changes to enhance the production of fertile cervical mucus, a key factor in boosting fertility.
Understanding the Role of Cervical Mucus in Fertility
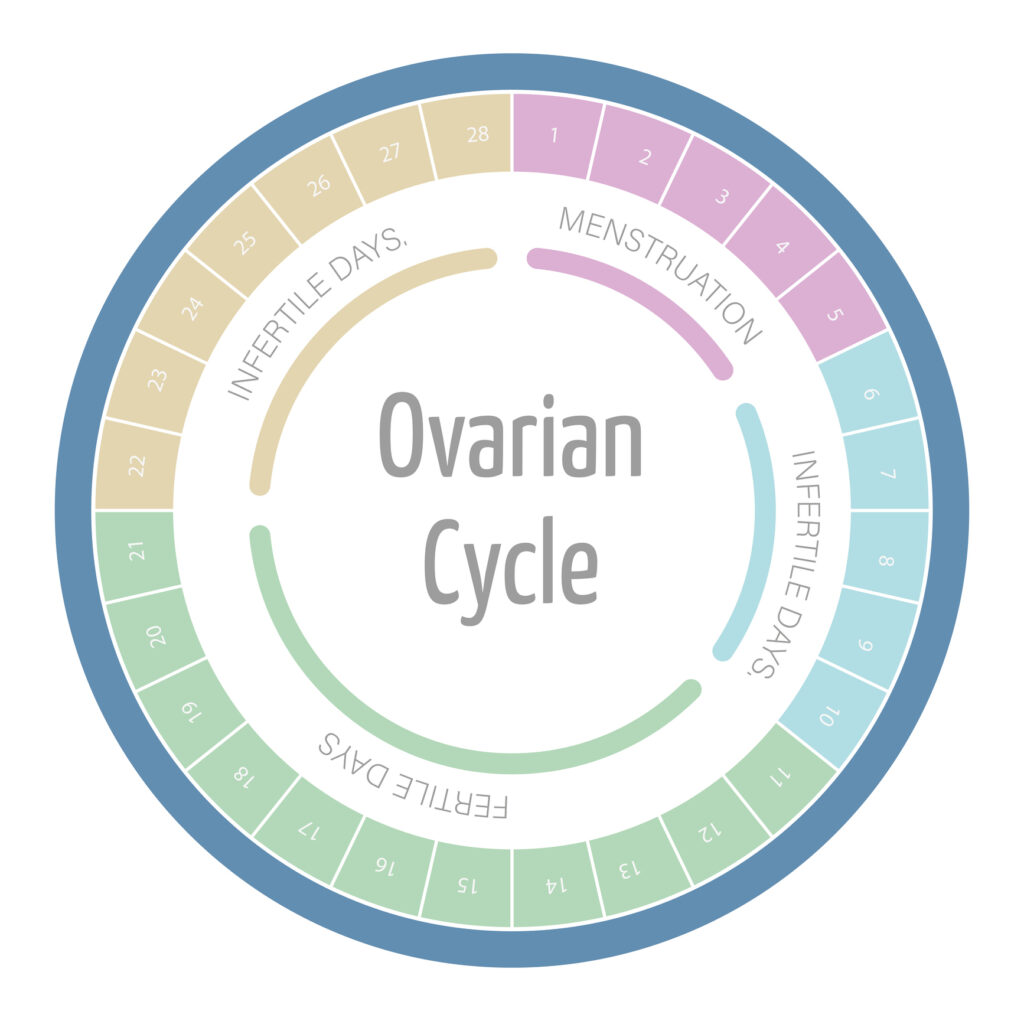
Cervical mucus is a vital fluid produced by the cervix. Its composition and quality are crucial indicators of a woman’s fertility. The presence and characteristics of cervical mucus change throughout the menstrual cycle, influenced by hormonal fluctuations, particularly estrogen and progesterone.
During the fertile window, which typically occurs around ovulation, cervical mucus becomes more abundant and stretchy, resembling raw egg whites. This fertile mucus plays a significant role in sperm transport, making it easier for sperm to navigate through the cervix and into the uterus for potential fertilization.
Understanding these changes is essential for women trying to conceive, as recognizing peak fertile mucus days can aid in timing intercourse for optimal chances of pregnancy.
In addition to its role in facilitating sperm movement, cervical mucus also serves as a protective barrier. During non-fertile phases, the mucus is thicker and more viscous, which helps to block harmful bacteria and pathogens from entering the uterus. This protective function is crucial for maintaining a healthy reproductive environment. Furthermore, the biochemical composition of cervical mucus can also provide insights into a woman’s overall reproductive health, as abnormalities in its consistency or volume may indicate underlying health issues that could affect fertility.
Women can track their cervical mucus changes by observing its texture and color throughout their menstrual cycle. Many find it helpful to combine this observation with other fertility awareness methods. These methods include tracking basal body temperature or using ovulation predictor kits. By doing so, they can create a comprehensive picture of their fertility patterns. This empowers them to make informed decisions about their reproductive health and family planning. This holistic approach not only enhances the chances of conception but also fosters a deeper understanding of one’s own body and its rhythms.
Dietary Changes to Enhance Cervical Mucus Production
Diet plays a crucial role in overall reproductive health, including the production of cervical mucus. A balanced diet rich in whole foods can positively impact the consistency and volume of cervical mucus.
- Increase Fluid Intake: Staying hydrated is fundamental. Water consumption supports all bodily functions, including mucus production.
- Include Healthy Fats: Foods rich in healthy fats help increase cervical mucus production due to their role in cellular health.
- Consume Whole Grains: Whole grains are high in fiber, which can improve hormonal balance and promote a healthy menstrual cycle.
Additionally, incorporating fruits and vegetables high in vitamins and antioxidants can help ensure your body has the nutrients it needs to support optimal reproductive functions. For instance, berries, citrus fruits, and leafy greens are excellent choices that not only provide essential vitamins but also help combat oxidative stress, which can negatively affect reproductive health. Moreover, foods rich in vitamin E, such as almonds and spinach, are known to enhance hormone production and may play a role in improving cervical mucus quality.
Furthermore, it’s important to consider the impact of certain lifestyle choices on cervical mucus production. Reducing processed foods and sugars can help stabilize blood sugar levels and hormonal balance. Which are vital for maintaining healthy mucus production. Additionally, incorporating regular physical activity can enhance circulation and support overall reproductive health. Activities such as yoga or moderate aerobic exercise can also help reduce stress. This is known to negatively affect hormonal balance and, consequently, cervical mucus production.
The Impact of Hydration on Mucus Quality
Hydration is key to maintaining the quality of cervical mucus. When the body is adequately hydrated, mucus becomes more elastic and conducive for sperm movement. Dehydration, on the other hand, can lead to thicker, less responsive cervical mucus, which may hinder fertility.
Experts recommend drinking plenty of water throughout the day, especially during the days leading up to ovulation. Herbal teas and other fluids can also contribute to overall hydration levels. But it’s essential to avoid excessive caffeine or alcohol intake, as these can dehydrate the body.
An easy way to gauge hydration levels is by monitoring the color of your urine. Pale straw-colored urine typically indicates adequate hydration, while darker urine may suggest a need for increased fluid intake.
In addition to water, certain foods can also enhance hydration and contribute positively to mucus quality. Fruits and vegetables with high water content, such as cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges, not only provide hydration but also deliver essential vitamins and minerals that support reproductive health. Incorporating these foods into your diet can be a delicious way to boost your fluid intake. This ensures your body has the nutrients it needs to produce healthy cervical mucus.
Moreover, the timing of hydration can play a significant role in its effectiveness. Drinking fluids consistently throughout the day rather than consuming large amounts at once can help maintain steady hydration levels. This is particularly important for women tracking their menstrual cycles. This is because optimal hydration can enhance the quality of cervical mucus during the fertile window. Understanding your body’s hydration needs and adjusting your intake accordingly can be a vital step in supporting reproductive health.
Supplements That May Boost Fertile Mucus
For those looking to enhance cervical mucus production, certain supplements may offer benefits. These supplements can help support hormonal balance and overall reproductive function. Adequate cervical mucus is crucial for fertility. It creates a conducive environment for sperm to travel through the cervix and into the uterus.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil, these can promote overall reproductive health and may enhance the quality of cervical mucus. Omega-3s are also known to reduce inflammation in the body, which can further support a healthy reproductive system.
- Vitamin E: This vitamin is known for its antioxidant properties and its role in reproductive health, potentially improving mucus production. Vitamin E may also help improve blood circulation to the reproductive organs, which can enhance overall fertility.
- B Vitamins: Especially B6 and B12, these vitamins support hormone regulation and can positively impact cervical mucus consistency. B vitamins are also essential for energy production and can help reduce stress, which is beneficial for those trying to conceive.
Consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements is advisable to ensure they are appropriate for your individual health needs. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as diet, hydration, and stress management play significant roles in cervical mucus production and overall fertility. Incorporating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide the necessary nutrients that support hormonal health. Staying well-hydrated is equally important, as adequate fluid intake can help maintain optimal mucus consistency.
Lifestyle Modifications for Optimal Cervical Health
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is critical for improving cervical health and enhancing mucus production. Regular exercise, stress management, and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly impact hormonal balance and reproductive function.

Engaging in regular physical activity helps improve blood circulation, including to the reproductive organs, which can enhance mucus production. Stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can also help balance hormones and improve overall health. These practices not only promote relaxation but also encourage mindfulness, allowing individuals to connect with their bodies and recognize the signs of hormonal changes more effectively.
Additionally, avoiding smoking and reducing exposure to environmental toxins can help maintain healthy hormone levels and cervical health, further supporting the production of fertile cervical mucus. It’s also beneficial to incorporate a diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, as these nutrients play a vital role in supporting reproductive health. Foods such as leafy greens, berries, nuts, and fatty fish can provide essential nutrients that help regulate hormonal levels and promote optimal cervical function.
The Importance of Hormonal Balance in Mucus Production
Maintaining hormonal balance is crucial for the production of quality cervical mucus. Fluctuations in hormones can lead to changes in mucus consistency, affecting its fertility-facilitating properties. Estrogen, in particular, plays a significant role in increasing the volume and elasticity of cervical mucus, which is essential for sperm mobility and survival. When estrogen levels are optimal, the mucus becomes more conducive to conception, creating a fertile environment that supports the journey of sperm toward the egg.
Monitoring your menstrual cycle and being aware of your body’s signals can help identify any hormonal imbalances. If you notice significant changes in cervical mucus or experience irregular cycles, it might be helpful to consult a healthcare provider for an evaluation. Tracking your cycle through methods like basal body temperature charting or using ovulation predictor kits can provide valuable insights into your hormonal fluctuations and overall reproductive health.
Natural methods to support hormonal balance include ensuring adequate sleep, managing stress, and considering dietary adjustments that promote hormonal health, such as incorporating more phytoestrogen-rich foods like flaxseeds and soy products. Additionally, regular physical activity can enhance hormonal regulation by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing stress levels. Engaging in activities like yoga or meditation can also be beneficial, as they help to lower cortisol levels, which can otherwise disrupt hormonal equilibrium.
Furthermore, it’s essential to stay hydrated, as proper hydration can influence mucus production. Drinking adequate amounts of water supports overall bodily functions, including the production of cervical mucus. Herbal teas, such as red clover or raspberry leaf, may also provide additional benefits by promoting hormonal balance and supporting reproductive health. By adopting a holistic approach that includes lifestyle changes, dietary considerations, and mindfulness practices, individuals can foster a more balanced hormonal environment conducive to optimal mucus production and fertility.
Timing and Techniques for Monitoring Cervical Mucus
Effective monitoring of cervical mucus can help pinpoint the most fertile days within your cycle. Observing changes in mucus can provide valuable insights into ovulation timing, which is essential for couples trying to conceive.
There are several techniques for tracking cervical mucus:
- Daily Observations: Each day, check the mucus by wiping the vaginal area with toilet paper or using a finger to assess its texture and appearance.
- Charting: Keep a calendar or a fertility tracking app to chart the changes in mucus consistency throughout the cycle.
- Combining Methods: Consider coupling mucus monitoring with basal body temperature tracking for a more comprehensive view of your fertile window.
By understanding and tracking cervical mucus changes, women can optimize their chances of conception by aligning intercourse with their most fertile days.
In conclusion, improving the production of fertile cervical mucus involves a multifaceted approach encompassing diet, hydration, supplementation, lifestyle choices, hormonal balance, and effective monitoring techniques. By paying attention to these aspects, women can enhance their fertility and take proactive steps toward conception.