Empower yourself with our comprehensive guide to taking charge of your fertility.
Taking Charge of Your Fertility: A Comprehensive Guide for Empowering Women
In today’s modern world, women have more options than ever when it comes to their reproductive health. However, with so much information available, it can be overwhelming to navigate the complexities of fertility. That’s why taking charge of your fertility and empowering yourself with knowledge is important. This comprehensive guide will provide you with the tools you need to understand your fertility, explore fertility awareness methods, consider lifestyle factors that impact fertility, and learn about medical interventions for fertility.
Understanding Your Fertility
When it comes to understanding your fertility, there are a few key concepts to grasp. The first is the basics of female fertility. It’s essential to understand how your body works and what factors contribute to fertility. From the menstrual cycle to ovulation, knowing the ins and outs of your reproductive system can help you make informed decisions about your fertility.
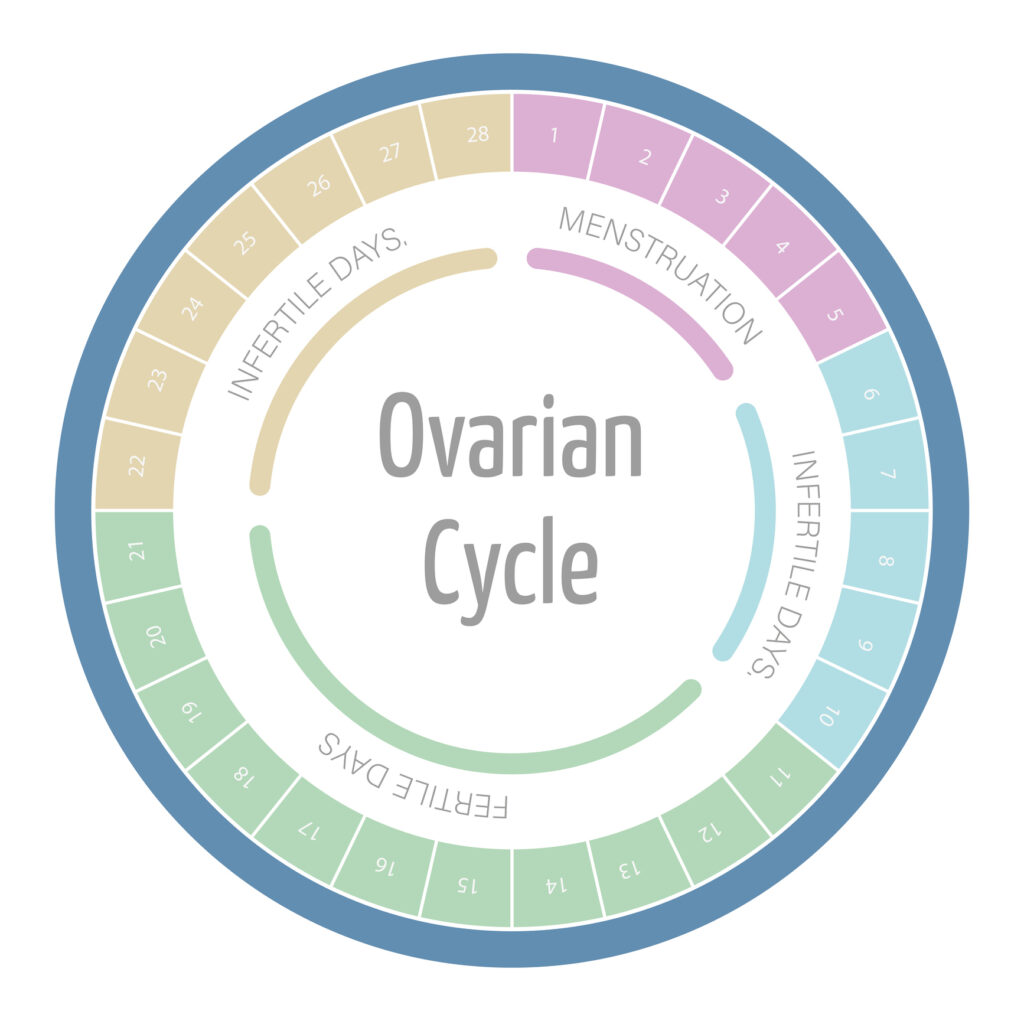
The menstrual cycle, which typically lasts around 28 days, is a complex process that involves the release of hormones and the shedding of the uterine lining. Understanding the different phases of the menstrual cycle, including menstruation, follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase, can provide valuable insights into your fertility. Each phase plays a crucial role in the overall reproductive process.
Ovulation, in particular, is a significant event in the menstrual cycle. It is the release of a mature egg from the ovary, ready to be fertilized by sperm. Ovulation usually occurs around the middle of the menstrual cycle, but it can vary from woman to woman. Tracking your ovulation can help you identify your most fertile days and increase your chances of conception.
Another important aspect of understanding your fertility is recognizing the impact of age. As women age, their fertility naturally declines. It’s crucial to be aware of this fact and plan accordingly if you want to conceive in the future. The decline in fertility is primarily due to a decrease in the number and quality of eggs in the ovaries. By the age of 35, a woman’s fertility starts to decline more rapidly, making it harder to conceive.
Being armed with this knowledge allows you to make proactive choices to preserve your fertility, such as considering fertility preservation options. Freezing your eggs, for example, can be an effective way to preserve your fertility and increase your chances of conceiving later in life. This option is particularly beneficial for women who may want to delay starting a family due to career or personal reasons.
Understanding your fertility also involves being aware of the various factors that can affect it. Lifestyle choices, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor diet, can have a negative impact on fertility. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and managing stress, can help optimize your fertility.
Furthermore, certain medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or endometriosis, can affect fertility. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns about your fertility or if you have been trying to conceive without success. They can provide guidance, perform necessary tests, and recommend appropriate treatments or interventions.
In conclusion, understanding your fertility is a multifaceted process that involves knowledge of your reproductive system, awareness of the impact of age, consideration of fertility preservation options, and attention to lifestyle and medical factors. By expanding your understanding of fertility, you can make informed decisions and take proactive steps to optimize your chances of conceiving when the time is right.
Fertility Awareness Methods
Fertility awareness methods are a natural and non-invasive way to track your menstrual cycle and increase your chances of conception. By understanding the different markers that determine fertility, you can gain valuable insights into your reproductive health.
One of the most common fertility awareness methods is tracking your menstrual cycle. This involves keeping a record of the length and regularity of your cycles, allowing you to identify patterns and predict when you’re most fertile. By understanding your cycle, you can optimize your chances of conceiving or effectively avoid pregnancy.
However, tracking your cycle is just the beginning. There are other factors that can provide valuable information about your fertility. One such factor is monitoring your basal body temperature. Your basal body temperature subtly fluctuates throughout your menstrual cycle, and a slight increase can indicate that ovulation has occurred. By tracking these temperature changes, you can pinpoint your most fertile days with greater accuracy.
Another important factor to consider when tracking your fertility is cervical mucus. The consistency and appearance of your cervical mucus change throughout your cycle, and these changes can help you determine your fertile window. During the fertile period, the mucus becomes clear, slippery, and stretchy, resembling raw egg whites. By paying attention to these changes, you can identify the optimal time for conception.
It’s worth noting that fertility awareness methods are not foolproof and may not be suitable for everyone. They require dedication, consistency, and a thorough understanding of your body. It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or fertility specialist to ensure you’re using these methods correctly and effectively.
In addition to tracking your menstrual cycle, basal body temperature, and cervical mucus, there are other supplementary methods that can enhance your fertility awareness. These include monitoring changes in your cervix position and texture, using ovulation predictor kits, and even incorporating lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise. The more information you gather and analyze, the better equipped you’ll be to make informed decisions about your reproductive health.
Ultimately, fertility awareness methods empower individuals to take an active role in their reproductive journey. By understanding the intricacies of their menstrual cycle and fertility, they can optimize their chances of conception or effectively prevent pregnancy. It’s an empowering and natural approach that allows individuals to connect with their bodies on a deeper level.
Lifestyle Factors and Fertility
Understanding your fertility and utilizing fertility awareness methods are crucial steps in your journey towards parenthood. However, it’s important to recognize that there are other factors at play that can impact your reproductive health. Lifestyle choices, such as nutrition, exercise, and stress management, can all have a significant influence on your fertility.
Let’s start with nutrition. The food you consume plays a vital role in supporting healthy hormone levels and promoting optimal fertility. A well-balanced diet that includes essential nutrients can provide your body with the fuel it needs to function at its best. Incorporating fertility-boosting foods into your meals can be particularly beneficial. For example, leafy greens like spinach and kale are rich in folate, a nutrient that has been linked to improved fertility. Whole grains, such as quinoa and brown rice, can provide a steady release of energy and help regulate blood sugar levels, which is important for reproductive health. Additionally, lean proteins like chicken, fish, and tofu are excellent sources of amino acids, which are the building blocks of hormones.
Exercise is another lifestyle factor that can impact fertility. Regular physical activity is generally recommended for overall health, but it’s important to find a balance that works for you. Intense or excessive workouts can put stress on your body, potentially disrupting your menstrual cycle and affecting ovulation. It’s crucial to listen to your body and know your limits. Engaging in moderate exercise, such as brisk walking, swimming, or yoga, can be a great way to stay active without putting excessive strain on your reproductive system.
Stress management is also crucial when it comes to optimizing fertility. Stress can have a profound impact on your hormonal balance and interfere with ovulation. Finding effective stress management techniques is essential for creating an environment that is conducive to conception. Meditation and deep breathing exercises can help calm your mind and reduce stress levels. Yoga, with its combination of gentle movement and mindfulness, can also be a valuable tool in managing stress. Additionally, seeking support through counseling or joining a support group can provide you with the emotional guidance and coping strategies needed during your fertility journey.
Remember, understanding and addressing lifestyle factors that can impact your fertility is just as important as tracking your menstrual cycle and timing intercourse. By nourishing your body with fertility-boosting foods, engaging in moderate exercise, and managing stress effectively, you can create an environment that supports optimal reproductive health.
Medical Interventions for Fertility
In some cases, medical interventions may be necessary to address fertility challenges. Before pursuing any medical interventions, it’s essential to undergo fertility testing. This includes various tests that can help identify potential causes of infertility.
During fertility testing, you may undergo a series of examinations and screenings to assess your reproductive health. These tests can include blood work to check hormone levels, ultrasound scans to evaluate the condition of your ovaries and uterus, and semen analysis to assess sperm quality. Additionally, your doctor may recommend a hysterosalpingogram, a procedure that uses dye and X-rays to examine the fallopian tubes and uterus for any blockages or abnormalities.
Once the cause of infertility is determined, fertility treatment options can be explored. Fertility medications, such as Clomiphene citrate or Letrozole, may be prescribed to stimulate ovulation in women with irregular menstrual cycles or hormonal imbalances. These medications work by regulating hormone levels and promoting the development of mature eggs.
If medication alone is not sufficient, assisted reproductive technologies (ART) can be considered. One of the most well-known ART procedures is in vitro fertilization (IVF). IVF involves the retrieval of eggs from the ovaries, fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory, and transferring the resulting embryos into the uterus. This procedure can be particularly helpful for individuals or couples with severe male factor infertility, blocked fallopian tubes, or unexplained infertility.
Aside from IVF, there are other ART procedures available, such as intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), where a single sperm is injected directly into an egg, and intrauterine insemination (IUI), where washed and concentrated sperm is placed directly into the uterus during ovulation.
It’s important to note that medical interventions for fertility can be both physically and emotionally demanding. The process of undergoing fertility treatments can involve frequent doctor visits, hormone injections, and monitoring of hormone levels and follicle development through ultrasound scans. These procedures can sometimes cause side effects, including bloating, mood swings, and fatigue.
Moreover, the emotional toll of fertility treatments should not be underestimated. The journey towards parenthood can be filled with hope, anticipation, and occasional disappointment. It’s crucial to have a strong support system in place, whether it’s through counseling, support groups, or leaning on loved ones who understand the challenges you may face.
Understanding the process, potential side effects, and success rates of different treatments is crucial when making informed decisions about your fertility journey. Your healthcare provider will guide you through the available options, discussing the benefits and risks associated with each treatment. They will also take into consideration your personal circumstances, medical history, and preferences to tailor a treatment plan that suits your needs.
It’s time to take charge of your fertility and empower yourself with knowledge. Understanding your fertility, exploring fertility awareness methods, considering lifestyle factors, and learning about medical interventions for fertility can give you the tools you need to make informed decisions and take control of your reproductive health. With this comprehensive guide, you can approach your fertility journey with confidence and embark on a path towards empowerment.