Learn about the odds and the success rates of IUI
IUI Success Rate, a Deeper Understanding
In the world of assisted reproductive technology, intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a popular fertility treatment option. But what exactly is IUI and how does it work? More importantly, what are the factors that influence IUI success rates? We will explore the ins and outs of IUI and provide you with valuable insights to help you understand the odds and improve your chances of success.

What is IUI and How Does It Work?
Intrauterine insemination, commonly referred to as IUI, is a fertility treatment procedure that involves placing sperm directly into a woman’s uterus. The goal of IUI is to increase the likelihood of fertilization by bringing sperm closer to the fallopian tubes. This procedure is typically performed around the time of ovulation to maximize the chances of conception.
The process of IUI begins with semen collection from the male partner or a donor. The semen sample is then washed and prepared in the laboratory to separate the healthy and motile sperm from the seminal fluid. The prepared sperm is then carefully inserted into the woman’s uterus using a long, thin catheter, which is guided through the cervix.
It is important for the woman to undergo a thorough evaluation of her reproductive health before undergoing IUI. This may include tests to assess her ovarian reserve, hormone levels, and the patency of her fallopian tubes. Additionally, the male partner’s sperm quality will also be assessed to ensure that it is suitable for the procedure.
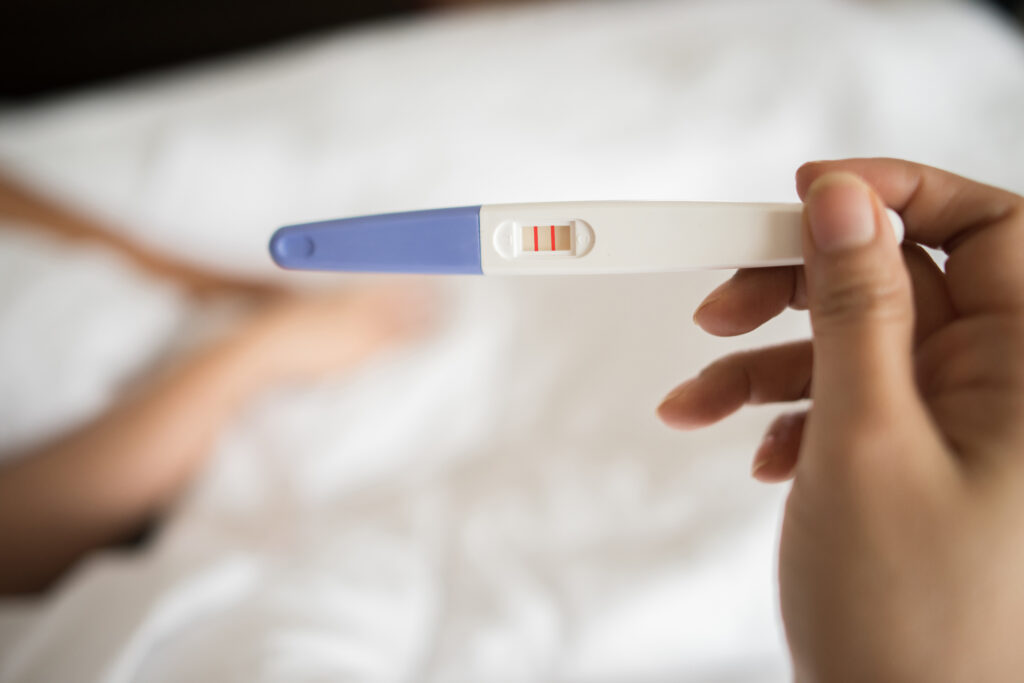
During the insemination process, the woman may experience mild cramping or discomfort, but these symptoms typically subside quickly. After the procedure, the woman is usually advised to rest for a short period before resuming normal activities. A pregnancy test is typically performed about two weeks after the insemination to determine if the procedure was successful.
Factors Influencing IUI Success Rates
It’s important to understand that the success rates can vary based on various factors. Let’s dive into the key factors that can influence the chances of a successful IUI treatment:
1. Age and Its Impact on IUI Outcomes
Age plays a significant role in the success of IUI. Women who are younger tend to have higher success rates compared to older women. This is because as women age, their ovarian reserve declines. This leads to a decrease in the quantity and quality of eggs available for fertilization. Therefore, it is important to consider age when assessing the potential success of IUI.
However, it’s worth noting that age is not the sole determining factor. Even though older women may have a lower chance of success, it doesn’t mean that IUI is not a viable option for them. Each individual’s situation is unique. Factors such as overall health, previous fertility history, and any underlying medical conditions should also be taken into account.
2. The Role of Sperm Quality in IUI Success
The quality of sperm used in IUI is crucial for achieving successful outcomes. Sperm motility, morphology (shape), and concentration all play important roles. A thorough semen analysis is typically performed to evaluate the sperm parameters before proceeding with IUI. In cases where the sperm quality is poor, alternative fertility treatments or techniques, such as using donor sperm or proceeding with in vitro fertilization (IVF), may be recommended.
It’s important to remember that male factor infertility can also impact the success rates of IUI. Issues such as low sperm count, poor motility, or abnormal morphology can decrease the chances of successful fertilization. However, advancements in assisted reproductive technologies have made it possible to overcome many of these challenges, offering hope to couples facing male factor infertility.
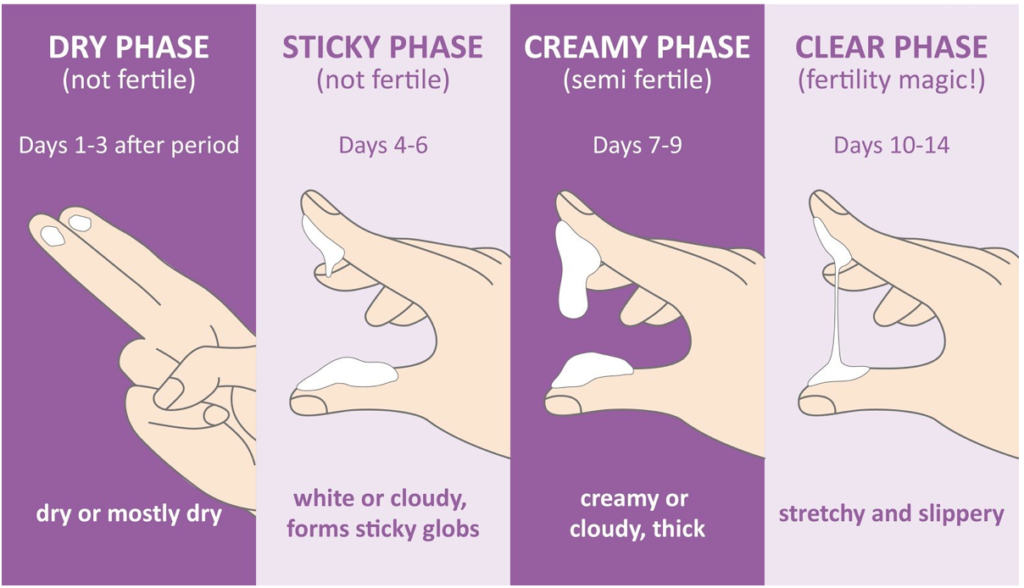
3. Timing: When is the Best Time for IUI?
Timing is crucial for the success of IUI. The procedure is typically scheduled around the time of ovulation, when the woman’s ovaries release a mature egg. Therefore, it’s essential to closely monitor the woman’s menstrual cycle and track ovulation. This is to ensure that IUI is performed at the optimal time. Ovulation can be detected through various methods, such as basal body temperature charting, ovulation predictor kits, or ultrasound monitoring.
In addition to timing the IUI procedure, it’s also important to consider the timing of any necessary fertility drugs. Medications such as clomiphene citrate or gonadotropins may be prescribed to stimulate the ovaries and increase the chances of successful ovulation. Careful monitoring and coordination with the healthcare team are crucial to ensure that the medications are administered at the right time and in the appropriate dosage.
By considering these factors and working closely with a fertility specialist, couples can make informed decisions about their IUI treatment and increase their chances of achieving a successful outcome. It’s important to remember that every individual’s journey is unique. What works for one couple may not work for another. However, with advancements in reproductive medicine and personalized care, the possibilities for building a family through IUI continue to expand.
Comparing IUI to Other Fertility Treatments
When considering fertility treatment options, it’s important to have a deeper understanding on how IUI compares to other available options. While IUI is a less invasive and more affordable option compared to procedures like in vitro fertilization, it may not be suitable for every couple. The success rates of IUI are generally lower than those of more advanced treatments, such as IVF. Therefore, it’s crucial to consult with a fertility specialist who can assess your specific situation. They can recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.
IUI can be a less stressful and physically demanding process compared to more complex fertility treatments. The procedure involves placing washed and processed sperm directly into the uterus. One can do this in a doctor’s office without the need for anesthesia. This simplicity and convenience make IUI a popular choice for couples who are just starting their fertility journey and want to explore less invasive options first.
However, it’s important to keep in mind that the effectiveness of IUI can vary depending on factors. Such as the woman’s age, overall health, and the underlying cause of infertility. While some couples may achieve success with IUI after a few cycles, others may need to explore alternative treatments if IUI proves to be unsuccessful. Ultimately, the decision on which fertility treatment to pursue should be based on a thorough evaluation of your individual circumstances and goals, with the guidance of a knowledgeable fertility specialist.
Emotional and Psychological Considerations During IUI
Undergoing any fertility treatment can be emotionally and psychologically challenging. The rollercoaster of hope and disappointment, coupled with the anxieties surrounding conception, can take a toll on individuals and relationships. It’s important to recognize and address these emotional challenges by seeking support from loved ones, joining support groups, or even considering counseling. Taking care of your emotional well-being during the IUI journey is vital for maintaining a positive outlook and reducing stress.
One common emotional aspect that individuals may experience during IUI is the feeling of isolation. It’s not uncommon to feel like you’re going through this journey alone, even if you have a supportive partner. The fact that fertility issues are often not openly discussed in society exacerbates this sense of isolation. Finding a community of individuals who are going through similar experiences can provide a sense of belonging and understanding that is crucial for emotional well-being.
Additionally, the process of undergoing IUI can bring up complex feelings of guilt and self-blame. Individuals may question their own bodies and feel responsible for the fertility challenges they are facing. It’s important to remember that infertility is a medical condition and not a personal failure. Seeking therapy or counseling can help individuals work through these feelings of guilt and develop healthier coping mechanisms. Remember, it’s okay to seek help and prioritize your mental health during this challenging time.

Tips to Improve Your Chances of Success with IUI
While there are no guarantees when it comes to fertility treatment, there are steps you can take to increase your chances of successful fertilization with IUI:
- Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding harmful habits such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption can improve your overall fertility.
- Take Fertility Supplements: Certain supplements, such as folic acid and coenzyme Q10, may enhance fertility and support reproductive health. However, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
- Follow Medication Protocols: If your fertility specialist prescribes medication to stimulate ovulation or support the uterine lining, it’s crucial to follow the recommended protocols diligently and attend all scheduled appointments.
- Minimize Stress: Stress can negatively impact fertility. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or pursuing hobbies can help create a more relaxed environment for conception.
- Communicate Openly: Establish clear and open communication with your partner and fertility specialist. Sharing your concerns, doubts, and fears can strengthen your support network and ensure that everyone is on the same page throughout the process.
Remember, each individual’s fertility journey is unique, and what works for one couple may not work for another. It’s essential to have realistic expectations, remain patient, and seek guidance from qualified healthcare professionals who can provide personalized advice tailored to your specific needs.
Lifestyle
When it comes to adopting a healthy lifestyle, it’s not just about what you eat, but also about how you eat. Taking the time to savor your meals and eat mindfully can have a positive impact on your overall well-being. Additionally, incorporating fertility-friendly foods into your diet, such as leafy greens, whole grains, and lean proteins, can provide your body with the necessary nutrients to support reproductive health.
In addition to fertility supplements, there are other natural remedies that you can explore to enhance your chances of success with IUI. Acupuncture, for example, has been shown to improve fertility outcomes by promoting blood flow to the reproductive organs and reducing stress levels. It’s worth considering complementary therapies like acupuncture as part of your overall fertility plan.
Conclusion
IUI is a widely-used fertility treatment option with varying success rates. Understanding the factors that influence these success rates, such as age, sperm quality, and timing, can help you make informed decisions and improve your chances of conceiving. It’s also important to consider the emotional aspects of undergoing IUI and to take steps to prioritize your well-being throughout the process. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, following medication protocols, and minimizing stress, you can optimize your chances of a positive outcome. Remember, fertility treatment is a journey, and with patience, support, and expert guidance, you can increase your odds of achieving your dream of starting a family.