Discover the signs of ovulation through changes in cervical mucus.
What does ovulation discharge look like?
Understanding your body’s natural rhythms can be crucial for monitoring fertility and recognizing ovulation. One of the most significant indicators of ovulation is the change in cervical discharge. In this article, we will explore various aspects of cervical mucus, including its appearance, significance, and how it can help you track your menstrual cycle effectively.
Understanding the Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is typically divided into four phases: the menstrual phase, the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase. Understanding these phases can help illuminate the changes that occur in cervical mucus throughout the cycle.
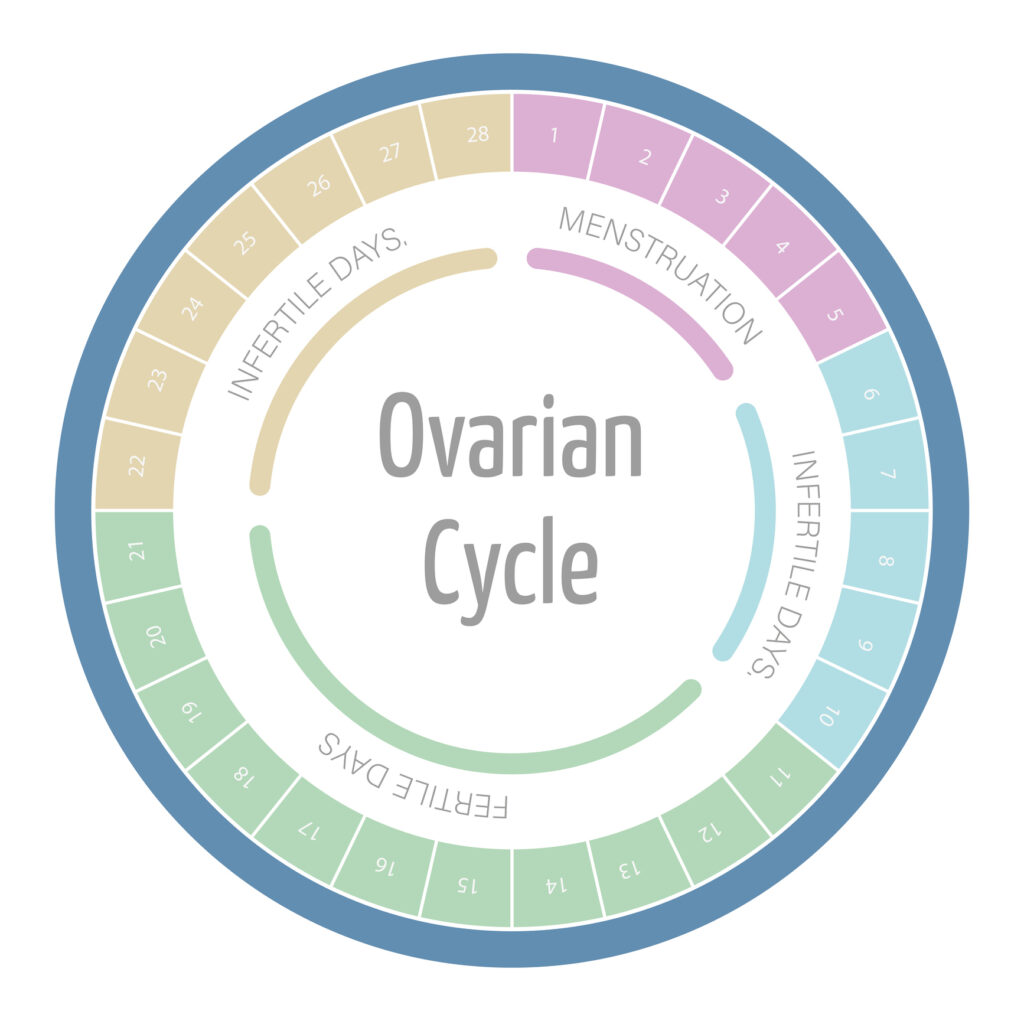
During the menstrual phase, the body sheds the uterine lining along with blood and fluid. This phase lasts about 3 to 7 days. Following this, the follicular phase begins, where hormones stimulate the maturation of follicles in the ovaries. As the follicles develop, they produce increasing amounts of estrogen, which plays a crucial role in thickening the uterine lining in preparation for a potential pregnancy. This phase is characterized by a gradual increase in energy levels and a shift in mood for many individuals, often attributed to the rising estrogen levels.
Ovulation occurs approximately midway through the cycle, when a mature egg is released. This is often marked by a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH), which triggers the release of the egg from the ovary. The cervical mucus during this time becomes clear, stretchy, and similar to raw egg whites, creating an optimal environment for sperm to travel through the cervix. This phase is often accompanied by heightened libido and increased sensitivity, as the body is primed for conception.
The luteal phase follows ovulation, during which the body prepares for potential pregnancy. If fertilization does not occur, the levels of hormones such as progesterone rise and then fall, leading to the eventual breakdown of the uterine lining. This phase typically lasts around 14 days and can bring about various symptoms, including premenstrual syndrome (PMS), which may manifest as mood swings, bloating, and breast tenderness. The cervical mucus during the luteal phase becomes thicker and less abundant. It serves as a barrier to sperm and pathogens as the body transitions back into the menstrual phase.
The Role of Cervical Mucus in Ovulation
Cervical mucus plays a vital role in conception and fertility. It is produced by the cervix, and its characteristics change dramatically throughout the menstrual cycle, influenced by hormonal fluctuations.
During ovulation, the increase in estrogen levels causes cervical mucus to become more abundant, clear, and stretchy, resembling raw egg whites. This type of mucus facilitates sperm movement through the cervix and into the uterus, enhancing the chances of fertilization.
In the days leading up to ovulation, the body prepares for this critical moment by creating an optimal environment for sperm survival. The consistency of cervical mucus not only aids in sperm transport but also serves as a protective barrier. It filters out non-viable sperm and pathogens. This selective mechanism ensures that only the healthiest sperm can navigate through the cervical canal. This increases the likelihood of successful fertilization. Additionally, the alkaline nature of fertile cervical mucus neutralizes the acidic environment of the vagina, which can be hostile to sperm. This further promotes their viability and motility.
After ovulation, as progesterone levels rise, the cervical mucus thickens and becomes more opaque, creating a barrier that helps to prevent additional sperm from entering the uterus. This change signals the body that ovulation has occurred and prepares it for a potential pregnancy. Understanding these changes can be beneficial for individuals tracking their fertility, as monitoring the quality and quantity of cervical mucus can provide valuable insights into their ovulation patterns and overall reproductive health.
Identifying Changes in Discharge During Ovulation
Recognizing the changes in discharge during ovulation can be an effective way to monitor fertility. Many women notice that their discharge becomes slippery and stretchy as they approach ovulation, making it easier to identify fertile windows. This type of discharge, often described as resembling raw egg whites, is produced by the cervical mucus, which plays a crucial role in facilitating sperm movement through the reproductive tract. Understanding this pattern can empower women to take charge of their reproductive health.
Tracking these changes can help women understand their cycles better. Regular observation of discharge can lead to informed decisions about timing intercourse for conception or using natural family planning methods. In addition to the texture, the volume and color of the discharge can also provide insights into hormonal fluctuations. For instance, some women may notice an increase in the amount of discharge. This can be a sign of heightened fertility. Keeping a journal or using a fertility app to log these observations can enhance awareness and contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of one’s menstrual cycle.
Moreover, it’s important to note that while changes in discharge are a common indicator of ovulation, they can vary significantly from woman to woman. Factors such as hydration levels, diet, and overall health can influence the characteristics of cervical mucus. For those who may not experience noticeable changes, other methods, such as tracking basal body temperature or using ovulation predictor kits, can complement the observation of discharge. By combining these techniques, women can gain a clearer picture of their ovulatory patterns, ultimately leading to more effective family planning strategies.
Color and Consistency: What to Expect
The appearance of cervical mucus can vary, but it is commonly characterized by a clear, stretchy consistency. This discharge is typically less viscous than other types and may be slightly cloudy. During the ovulation phase of the menstrual cycle, the body produces more estrogen, which stimulates the cervical glands to create this fertile mucus. This change in discharge is nature’s way of preparing the body for potential conception, as the stretchy quality helps sperm travel more easily through the cervix.
While clear mucus is often a sign of ovulation, other colors can appear as well. For instance, some women may notice a slight white or yellowish tint, which is generally not a cause for concern. This variation can be influenced by factors such as hydration levels, hormonal fluctuations, and even diet. However, if the mucus has a strong odor or is accompanied by itching or irritation, it may indicate an infection. It’s essential to pay attention to these signs, as they can provide valuable insights into your reproductive health.
In addition to color and consistency, the volume of discharge can also change throughout the menstrual cycle. Many women report an increase in the amount of discharge during ovulation, which can be a helpful indicator for those tracking their fertility. Keeping a journal of your cycle can help you recognize these changes over time, making it easier to identify when you are most fertile or if something seems off.
Furthermore, lifestyle factors such as stress, exercise, and diet can also impact the characteristics of cervical mucus. For example, high levels of stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that might alter the consistency or amount of cervical mucus produced. Similarly, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can promote optimal hormonal function, potentially leading to clearer and more abundant discharge during ovulation. Understanding these influences can empower women to take charge of their reproductive health and make informed decisions regarding their fertility awareness.
Common Myths
Many myths surround cervical mucus, which can lead to confusion among women. One common misconception is that all women experience discharge that is identical during ovulation.
In reality, the amount and consistency of discharge can differ significantly from woman to woman. Another myth is that a lack of noticeable discharge indicates that a woman is not ovulating, while in some cases, discharge may be less noticeable if a woman’s hormonal levels are imbalanced.
How to Track Your Ovulation Through Discharge
Tracking ovulation through discharge is an accessible method that can empower women to take control of their reproductive health. To begin tracking, consider the following steps:
- Observe and record the characteristics of your discharge daily.
- Take note of when the discharge changes to a clearer, stretchier form.
- Combine this information with other methods, such as basal body temperature measurement.
By keeping a detailed record, you can predict your fertile window more accurately and improve your chances of conception.
When to Seek Medical Advice About Discharge
While some variations in cervical mucus are normal, there are situations in which women should seek medical attention. If you notice any of the following, it may be time for a check-up:
- Your discharge has a strong, unpleasant odor.
- There is a significant change in color, such as green or brown.
- You experience any accompanying symptoms such as itching, burning, or irritation.
These symptoms could indicate an infection or other health concerns that require professional assessment.
The Impact of Hormones on Discharge Appearance
Hormonal changes throughout the menstrual cycle profoundly impact the appearance and consistency of cervical mucus. Estrogen levels rise before ovulation, leading to the production of thinner, more stretchable mucus.
Conversely, during the luteal phase, progesterone levels increase, which changes the mucus to a thicker and cloudier consistency. Understanding these hormonal fluctuations can help women interpret changes in discharge more accurately.
Comparing Cervical Discharge to Other Types
Ovulation discharge can vary throughout the menstrual cycle, not just during ovulation. In addition to the fertile mucus seen during ovulation, women also experience thicker, sticky discharge right after menstruation and creamy or cloudy discharge during the luteal phase.
Knowing the differences between these types of discharge can help women better understand their own bodies. For instance, while fertile mucus promotes sperm movement, the thicker mucus post-ovulation may block sperm passage if pregnancy does not occur.
Tips for Monitoring Your Fertility Through Discharge
Monitoring discharge to track ovulation can be straightforward, but here are some useful tips to enhance your fertility awareness:
- Keep a daily journal or use a fertility tracking app to note changes in your discharge.
- Check your discharge multiple times a day, as characteristics can vary throughout the day.
- Pair your observations with other fertility tracking methods for comprehensive insight into your cycle.
By following these tips, you can gain a better understanding of your fertility patterns and make informed decisions regarding conception or family planning.
In conclusion, recognizing the changes in cervical mucus can play a crucial role in understanding your menstrual cycle and tracking fertility. By dispensing with common myths and adopting practical tracking techniques, you empower yourself with knowledge about your reproductive health.