Uncover the complexities of diagnosing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) with our comprehensive guide.
Diagnosing PCOS: A Comprehensive Guide
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects many women of reproductive age. Although it has no known cure, early diagnosis and effective management can significantly improve a woman’s quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various aspects of diagnosing PCOS, from understanding the condition to interpreting your test results and exploring treatment options.
Understanding PCOS
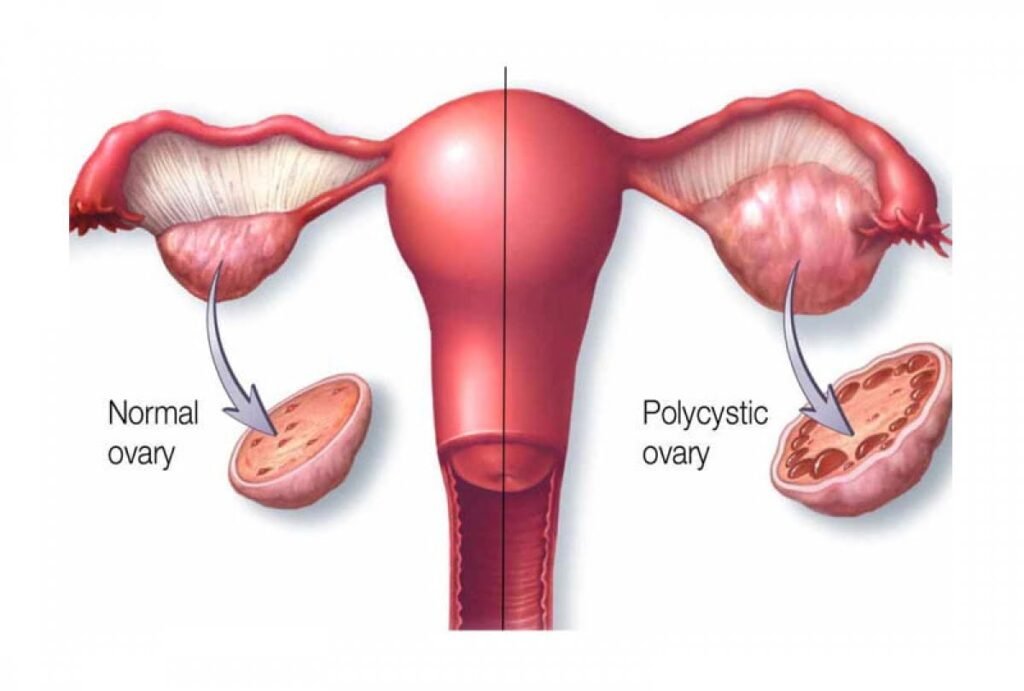
What is PCOS?
PCOS is a complex hormonal disorder that affects the ovaries, leading to the development of multiple cysts. These cysts are small, fluid-filled sacs that can form in the ovaries. PCOS is characterized by an imbalance of female sex hormones, specifically increased levels of androgens (male hormones) and fluctuations in insulin levels.
Common Symptoms of PCOS
The symptoms of PCOS can vary among women, but some common signs include irregular menstrual cycles, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), acne, and weight gain. Many women with PCOS also experience fertility issues due to irregular ovulation.
Long-Term Health Implications of PCOS
PCOS is not just a reproductive disorder; it can also have long-term health implications. Women with PCOS have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease. In addition, PCOS has been linked to mental health issues such as anxiety and depression.
While the physical symptoms of PCOS are often the most visible and well-known, it is important to recognize the impact this condition can have on a woman’s emotional well-being. Living with PCOS can be challenging, as it can affect self-esteem and body image. The hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS can contribute to mood swings, irritability, and feelings of sadness or hopelessness. It is crucial for women with PCOS to seek emotional support and practice self-care to help manage these aspects of their health.
Furthermore, PCOS is a condition that requires ongoing management and monitoring. Women with PCOS often need to make lifestyle changes to manage their symptoms and reduce their risk of long-term health complications. This may include adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and taking medications to regulate hormones or manage associated conditions such as insulin resistance. Regular visits to healthcare professionals, such as gynecologists and endocrinologists, are essential for monitoring the condition and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
The Diagnostic Process for PCOS
Medical History and Physical Examination
When diagnosing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), your healthcare provider will start by taking a detailed medical history and performing a thorough physical examination. This comprehensive approach allows them to gather important information about your symptoms, menstrual cycle patterns, and any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to your symptoms. The medical history will provide valuable insights into your overall health and help guide the diagnostic process.
During the physical exam, your healthcare provider will carefully assess your body for any signs of PCOS. They may check for hirsutism, which is the excessive growth of hair in areas such as the face, chest, and back. Acne, another common symptom of PCOS, will also be evaluated. Additionally, they will pay close attention to any weight gain you may have experienced, as this can be associated with PCOS.
Laboratory Tests for PCOS
To confirm a PCOS diagnosis, your healthcare provider may order blood tests to measure hormone levels. These tests are crucial in assessing the balance of hormones in your body. Hormones such as testosterone, estrogen, and luteinizing hormone (LH) will be evaluated to determine if any imbalances are present. Additionally, your blood sugar and insulin levels may be checked to evaluate for insulin resistance, a common condition in PCOS. These tests will provide valuable information about your body’s metabolic function and help in confirming the diagnosis.
Imaging Studies in PCOS Diagnosis
In some cases, imaging studies may be necessary to further assess the ovaries and rule out other conditions. Transvaginal ultrasound is a commonly used imaging technique to visualize the ovaries and detect the presence of cysts. This non-invasive procedure involves the use of a small probe inserted into the vagina to obtain detailed images of the ovaries. The ultrasound can help your healthcare provider evaluate the size and appearance of the ovaries, as well as identify any cysts that may be present.
In certain situations, your healthcare provider may decide that additional imaging techniques are needed for a more comprehensive evaluation. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide detailed images of the pelvic region, allowing for a closer examination of the ovaries and surrounding structures. Pelvic laparoscopy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure, may also be recommended in some cases. This procedure involves the insertion of a thin tube with a camera into the abdomen to directly visualize the ovaries and other pelvic organs. These additional imaging studies can provide valuable information to aid in the diagnosis and management of PCOS.
Interpreting Your PCOS Diagnosis
Understanding Your Test Results
Once you have completed the necessary tests, your healthcare provider will interpret the results and explain them to you. They will discuss the hormone levels, insulin resistance, and any other findings relevant to your PCOS diagnosis. It’s important to ask questions and seek clarification if there’s anything you don’t understand.
What Does a PCOS Diagnosis Mean?
Receiving a PCOS diagnosis can be overwhelming, but it’s important to remember that it is a manageable condition. Your healthcare provider will explain how PCOS may impact your overall health and fertility. They will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan to address your symptoms and minimize long-term health risks.
Understanding the implications of a PCOS diagnosis can be a complex process. It’s not just about knowing the medical jargon or understanding the test results; it’s about comprehending how this condition can affect your daily life and future plans. That’s why it’s crucial to have open and honest communication with your healthcare provider. They are there to guide you through this journey and provide you with the necessary information to make informed decisions.
During your discussion with your healthcare provider, they will explain the hormone levels associated with PCOS. Hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone play a significant role in regulating various bodily functions. Understanding how these hormone imbalances can contribute to the symptoms of PCOS is essential in managing the condition effectively.
Treatment Options for PCOS
Lifestyle Modifications for Managing PCOS
Lifestyle modifications play a key role in managing PCOS. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can help improve hormone balance and reduce insulin resistance. Your healthcare provider may offer guidance on specific dietary recommendations, exercise routines, and stress management techniques.
Medications Used in PCOS Treatment
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage the symptoms of PCOS. Birth control pills, for example, can help regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce excess hair growth. Anti-androgen medications may also be used to address hirsutism and acne. Additionally, insulin-sensitizing drugs can be prescribed to manage insulin resistance.
Surgical Interventions for PCOS
In certain situations, surgical interventions may be recommended for PCOS treatment. Ovarian drilling is a minimally invasive procedure in which small holes are made in the ovaries using lasers or heat. This procedure can restore ovulation and improve fertility in women with PCOS. However, it is typically considered as a last resort when other treatment options have been unsuccessful.
While lifestyle modifications and medications are often the first line of treatment for PCOS, it’s important to explore all available options. In addition to these approaches, there are other complementary therapies that can be considered. For instance, acupuncture has been shown to have positive effects on hormone regulation and menstrual regularity in women with PCOS. By stimulating specific points on the body, acupuncture can help restore balance and improve overall well-being.
Another alternative treatment option for PCOS is herbal medicine. Certain herbs, such as saw palmetto and chasteberry, have been traditionally used to support hormonal balance and regulate menstrual cycles. However, it’s crucial to consult with a qualified herbalist or healthcare provider before incorporating herbal remedies into your PCOS treatment plan, as they can interact with other medications or have potential side effects.
In conclusion, diagnosing PCOS involves understanding the condition, undergoing a series of tests, and interpreting the results. While receiving a PCOS diagnosis can be challenging, there are various treatment options available to manage the symptoms and reduce the long-term health risks associated with this hormonal disorder. By working closely with healthcare professionals and making necessary lifestyle modifications, women with PCOS can lead fulfilling lives and maintain their overall well-being. Exploring complementary therapies, such as acupuncture and herbal medicine, may also provide additional support in managing PCOS symptoms. Remember, every individual is unique, and finding the right combination of treatments may require some trial and error. With patience and perseverance, it is possible to find an effective treatment plan that works for you.




