Discover how HCG shots can benefit men’s health in this comprehensive article.
The Benefits of HCG Shot for Men
The use of HCG shots for men is gaining popularity due to their potential benefits. HCG, or human chorionic gonadotropin, is a hormone that plays a crucial role in the male body. Understanding how HCG functions and the benefits it offers can help men make informed decisions about incorporating HCG shots into their health regimen.
Understanding HCG and Its Role in the Male Body
Before delving into the benefits of HCG shots for men, it is important to understand what HCG is and how it functions in the male body. HCG is a hormone that is naturally produced in both men and women. In women, it is primarily associated with pregnancy, as it helps in the development of the placenta and sustains the pregnancy. However, HCG also has important functions in the male body.
In men, HCG plays a vital role in stimulating the production of testosterone. Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and is responsible for various aspects of male health, including sexual function, muscle development, and bone density. By stimulating testosterone production, HCG helps maintain overall health and well-being in men.
What is HCG?
HCG, or human chorionic gonadotropin, is a hormone that is naturally produced in the body. It is commonly associated with pregnancy, but it also has important functions in the male body. HCG is available in the form of injections, which are commonly referred to as HCG shots.
How Does HCG Function in Men?
In men, HCG stimulates the production of testosterone. Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and is responsible for various aspects of male health, including sexual function, muscle development, and bone density. By boosting testosterone levels, HCG helps enhance overall well-being and vitality in men.
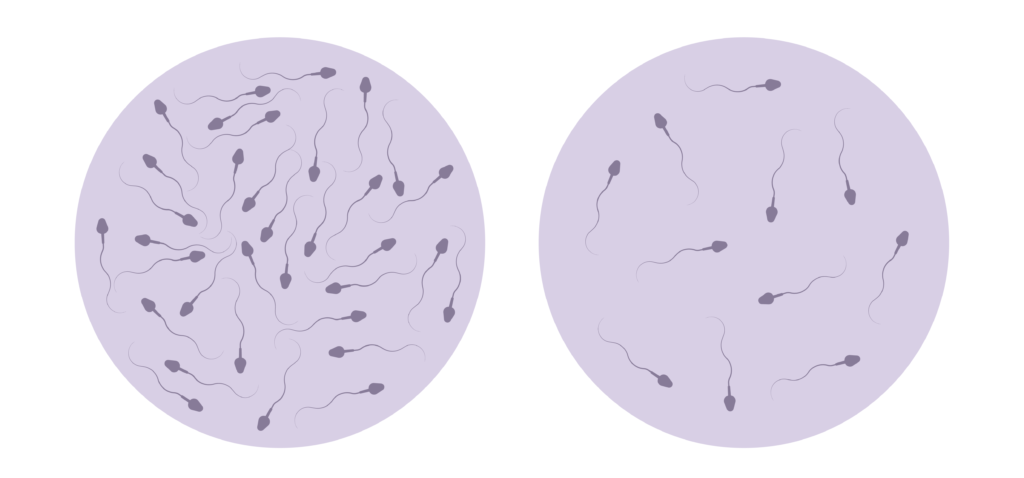
Furthermore, HCG has been found to play a role in fertility in men. It can help improve sperm production and quality, which is crucial for men experiencing infertility issues. By increasing testosterone levels and improving sperm quality, HCG can aid in enhancing male fertility.
Another important function of HCG in men is its ability to support weight loss and muscle gain. When used in conjunction with a healthy diet and exercise regimen, HCG injections can help promote fat loss while preserving lean muscle mass. This makes HCG a popular choice among men looking to improve their body composition and overall physical performance.
Delving into the Benefits of HCG Shots for Men
Now that we understand the role of HCG in the male body, let’s explore the specific benefits that HCG shots can provide for men.
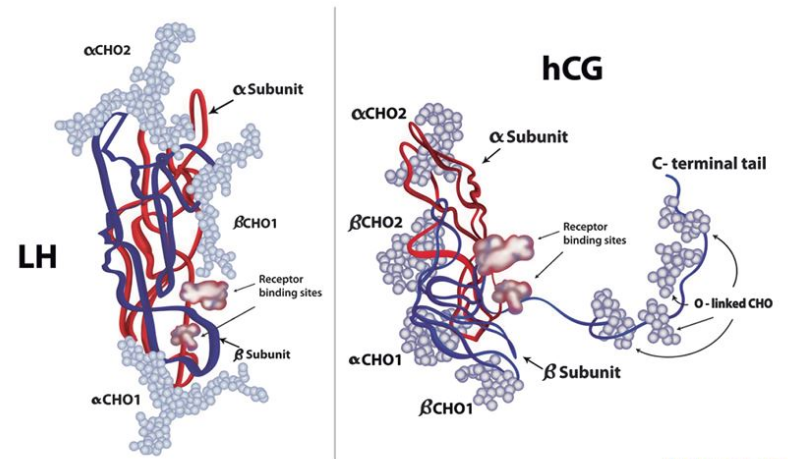
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is a hormone that plays a crucial role in the male body by mimicking the luteinizing hormone (LH), which stimulates the production of testosterone in the testes. This process is essential for maintaining male characteristics, such as muscle mass, bone density, and libido.
Boosting Testosterone Levels
One of the primary benefits of HCG shots for men is the ability to boost testosterone levels. Low testosterone, or hypogonadism, can lead to a range of symptoms, including decreased libido, fatigue, muscle loss, and mood changes. By stimulating testosterone production, HCG shots can help alleviate these symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Furthermore, optimal testosterone levels are vital for men’s health and vitality. Testosterone not only affects physical attributes but also plays a significant role in mental health, energy levels, and overall quality of life.
Enhancing Fertility
HCG is also known for its role in improving fertility in men. For men who are struggling with infertility issues, HCG shots can help stimulate the production of sperm and increase the chances of a successful pregnancy. This can be particularly beneficial for couples who are trying to conceive.
Moreover, HCG therapy can be a valuable option for men with low sperm count or poor sperm motility, as it can enhance sperm production and quality, increasing the likelihood of conception.
Aiding in Weight Loss
HCG shots have also gained attention for their potential in aiding weight loss. When combined with a low-calorie diet, HCG shots can help promote fat loss while preserving muscle mass. This can result in more effective and sustainable weight loss, making it an attractive option for men who are looking to shed excess pounds.
Additionally, the combination of HCG shots and a calorie-restricted diet can help reset the metabolism, making it easier for individuals to maintain their weight loss results in the long term. This approach not only promotes fat loss but also encourages healthier eating habits and lifestyle changes.
The Science Behind HCG Shots
Understanding the science behind HCG shots can provide insights into how they work and their potential benefits. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is a hormone produced during pregnancy that has been used for various medical purposes, including weight loss and fertility treatments.
When it comes to weight loss, HCG shots are believed to help by reducing feelings of hunger and promoting fat loss. The hormone is thought to work by resetting the body’s metabolism and helping to mobilize stored fat for energy, leading to rapid weight loss when combined with a low-calorie diet.
The Process of HCG Administration
HCG shots are typically administered by a healthcare professional. The injections are given into the muscle or under the skin, depending on the specific instructions provided by the healthcare provider. The frequency and dosage of the shots may vary depending on individual needs and goals.
It is essential to follow the prescribed administration guidelines to ensure the effectiveness and safety of HCG shots. Patients are often advised to rotate injection sites to prevent irritation and ensure consistent absorption of the hormone.
How HCG Interacts with Male Hormones
HCG interacts with the male hormone system, specifically by stimulating the production of testosterone. By mimicking the action of luteinizing hormone (LH), HCG signals the testes to produce more testosterone. This increase in testosterone levels can have a range of positive effects on male health and well-being.
Increased testosterone levels can lead to improvements in muscle mass, energy levels, and libido. For men dealing with low testosterone levels, HCG shots may offer a natural way to boost hormone production and alleviate symptoms of hypogonadism.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of HCG Shots
While HCG shots offer potential benefits, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects and risks associated with their use. Understanding the full spectrum of effects can help individuals make informed decisions about their healthcare journey.
When considering the use of HCG shots, it is essential to delve into the nuances of their impact on the body. Beyond the immediate benefits, a thorough understanding of potential side effects and risks can empower individuals to navigate their treatment plan with confidence and clarity.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects of HCG shots may include redness, swelling, or pain at the injection site. Some individuals may also experience hormonal changes, such as mood swings or acne. It is important to discuss any potential side effects with a healthcare professional to ensure that they are properly managed. By fostering open communication with healthcare providers, individuals can address these common side effects proactively and tailor their treatment plan to suit their unique needs.
Furthermore, exploring the interplay between common side effects and individual health profiles can shed light on personalized approaches to mitigating discomfort and optimizing treatment outcomes.
Serious Risks and How to Mitigate Them
Although rare, there are some serious risks associated with HCG shots, especially when used improperly. These risks may include blood clots, allergic reactions, or hormonal imbalances. To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting HCG shots and to follow their guidance regarding dosage and administration. By prioritizing safety and adherence to medical advice, individuals can minimize the potential for serious risks and enhance the overall effectiveness of their treatment.
Delving into the mechanisms underlying these serious risks can provide individuals with a comprehensive understanding of the factors at play, enabling them to approach their treatment regimen with a well-rounded perspective. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can navigate the potential risks associated with HCG shots with vigilance and confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions about HCG Shots for Men
Here are some commonly asked questions about HCG shots for men:
Who Should Consider HCG Shots?
HCG shots may be considered by men who have low testosterone levels or are experiencing symptoms of hypogonadism. They may also be beneficial for men who are looking to enhance fertility or aid in weight loss. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if HCG shots are appropriate for individual needs and goals.
How Long Does It Take to See Results?
The timeline for seeing results from HCG shots will vary depending on various factors, including individual metabolism and hormone levels. Some men may start experiencing improvements in symptoms within a few weeks, while others may take longer. It is important to discuss expectations and timelines with a healthcare professional to ensure realistic goals and to monitor progress accurately.
Overall, HCG shots offer potential benefits for men, including boosting testosterone levels, enhancing fertility, and aiding in weight loss. Understanding the science behind HCG shots and being aware of the potential risks can help men make informed decisions about incorporating them into their health regimen. It is always important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if HCG shots are appropriate and safe for individual needs.
When considering HCG shots for men, it’s essential to understand the mechanism of action behind this treatment. HCG, or human chorionic gonadotropin, is a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating testosterone production in men. By stimulating the testes to produce more testosterone, HCG shots can help alleviate symptoms of low testosterone, such as fatigue, low libido, and muscle weakness.
Furthermore, for men looking to improve fertility, HCG shots can be a valuable option. HCG mimics the action of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the body, which is responsible for triggering ovulation in women and testosterone production in men. By promoting the production of testosterone, HCG can enhance sperm production and quality, increasing the chances of conception for couples struggling with infertility.