Curious about the possibility of getting pregnant during your period? This article explores the chances, risks, and factors that contribute to conception during menstruation.
Can You Get Pregnant on Your Period?
Many people have wondered whether it is possible to get pregnant during their period. The answer is not a simple yes or no. To understand the likelihood of pregnancy during menstruation, it is important to have a basic understanding of the average menstrual cycle.

Understanding the Menstrual Cycle
The average menstrual cycle is a natural process that occurs in women of reproductive age. It typically lasts for about 28 days, although the length can vary from person to person. The cycle consists of several phases, each of which plays a crucial role in a woman’s fertility.
Understanding the menstrual cycle is essential for women to track their reproductive health and fertility. By knowing the different phases and what happens during each, individuals can better understand their bodies and potential issues that may arise.
The Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is divided into four phases: menstruation, the follicular phase, ovulation, which is usually day 14, and the luteal phase which is up to the last 24 hours of your period. Menstruation is the shedding of the uterine lining, which occurs when an egg is not fertilized in the previous cycle. The follicular phase follows menstruation and is characterized by the development of follicles in the ovaries. Ovulation occurs when a mature egg is released from the ovary, while the luteal phase is the period of time between ovulation and the start of the next menstruation.
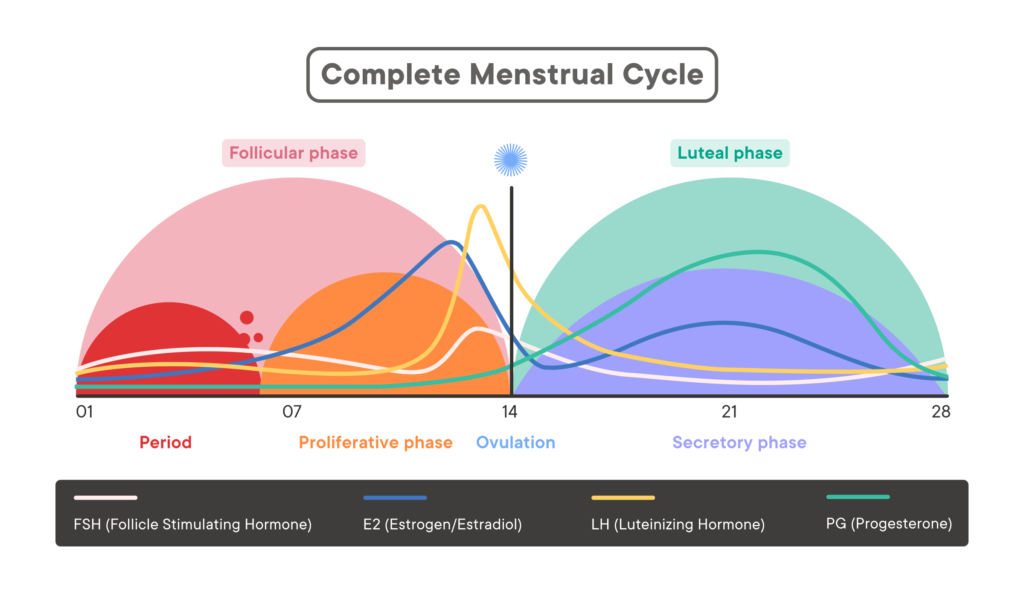
Each phase of the menstrual cycle is controlled by different hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, which fluctuate to prepare the body for potential pregnancy. These hormonal changes not only affect the reproductive system but can also impact mood, energy levels, and overall well-being.
How Ovulation Works
Ovulation is a key event in the menstrual cycle and is necessary for pregnancy to occur. It typically happens around the middle of the cycle, although this can vary. During ovulation, one of the ovaries release an egg and travels through the fallopian tube towards the uterus. If the egg is fertilized by sperm during this time, it may implant in the uterus lining and result in pregnancy.
Tracking ovulation is crucial for individuals trying to conceive or avoid pregnancy. There are various methods, such as tracking basal body temperature or using ovulation predictor kits, that can help determine the most fertile window during the menstrual cycle. Understanding ovulation can empower individuals to take control of their reproductive health and planned parenthood.
The Possibility of Pregnancy During Menstruation
While the likelihood of pregnancy is generally lower during menstruation, it is not impossible. Several factors play a role in determining the chances of getting pregnant if you have sex during this time.
It is important to note that the female reproductive system is a complex and intricate mechanism. Understanding the nuances of fertility can shed light on the potential for conception with unprotected sex during your period. While the menstrual cycle is often divided into distinct phases, the boundaries between them can sometimes blur, leading to unexpected outcomes.
The Lifespan of Sperm
Sperm can live inside the female reproductive system for up to five days. This means that if intercourse occurs towards the end of a woman’s period, the sperm can still be viable when ovulation occurs a few days later. If an egg is released and fertilized during this time, pregnancy is possible.
Furthermore, the journey of sperm through the female reproductive tract is a fascinating process. From navigating the acidic environment of the vagina to encountering various cervical mucus textures, sperm face numerous obstacles before reaching the fallopian tubes where fertilization takes place.
The Timing of Ovulation and Menstruation
While ovulation typically occurs around the middle of the cycle, it is not always predictable. Some women may experience irregular cycles, making it difficult to determine when ovulation will occur whether you ovulate early or late. Additionally, some women may have short cycles, meaning that ovulation could occur closer to the end of the period. In these cases, the chances of pregnancy during menstruation may be higher.
Moreover, the interplay between hormonal fluctuations and external factors can influence the timing of ovulation. Stress, diet, and lifestyle choices can all impact the regularity of a woman’s cycle, potentially shifting the window of fertility. Understanding these variables can provide insight into the intricate dance of hormones and their effects on reproductive health.
Factors That Increase the Chances of Pregnancy During Period
Several factors can increase the likelihood of getting pregnant during menstruation. These factors are worth considering for individuals who want to avoid an unplanned pregnancy.
Irregular Menstrual Cycles
Women with irregular menstrual cycles may find it difficult to predict when ovulation will occur. This uncertainty increases the chances of getting pregnant during menstruation if ovulation happens sooner than expected.
Short Menstrual Cycles
Some women have shorter cycles, which means that ovulation can occur closer to the end of their period. If intercourse happens towards the end of the menstrual cycle, there is a higher likelihood of pregnancy.
Additionally, certain lifestyle factors can also play a role in increasing the chances of pregnancy during menstruation. Factors such as stress, poor diet, lack of exercise, and inadequate sleep can disrupt hormonal balance, potentially leading to irregular ovulation and increasing the likelihood of conception during menstruation.
Cervical Mucus Changes
Changes in cervical mucus consistency can also impact the likelihood of pregnancy during menstruation. Fertile cervical mucus, which is clear, slippery, and stretchy, helps sperm travel to the egg more easily. If this type of mucus is present towards the end of a period and ovulate, it can enhance the chances of conception.
Common Misconceptions About Pregnancy and Menstruation
Many misconceptions exist regarding pregnancy and menstruation. It is important to separate fact from fiction to make informed decisions about contraception and reproductive health.
Understanding the complexities of the menstrual cycle and fertility can help individuals navigate their reproductive health with confidence and accuracy. Let’s delve deeper into some common misconceptions surrounding pregnancy and menstruation to shed light on these crucial topics.
The “Safe” Period Myth
Some people believe that there is a “safe” period during the menstrual cycle when it is impossible to get pregnant. This is not entirely accurate, as the timing of ovulation can vary, making conception possible at unexpected times.
It’s essential to recognize that sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days, increasing the window of fertility beyond ovulation. This highlights the importance of using reliable contraception methods consistently to prevent unintended pregnancies.
The Impact of Menstrual Flow on Fertility
Contrary to popular belief, the presence of menstrual blood or vaginal bleeding does not prevent pregnancy. Sperm can still travel through the cervix and fertilize an egg during menstruation, especially towards the end of the period.
Additionally, irregular menstrual cycles can pose challenges when predicting fertile days, emphasizing the need for personalized fertility awareness methods or medical guidance for individuals trying to conceive or avoid pregnancy. By dispelling these misconceptions, individuals can make informed choices about their reproductive health and well-being.
Precautions and Birth Control Methods
To avoid the risk of unplanned pregnancy, it is essential to take appropriate precautions. There are several birth control methods available, birth control pills for one, that can help individuals manage their fertility.
Understanding the importance of contraception is vital for individuals who wish to prevent unintended pregnancies. By utilizing various birth control methods, individuals can take control of their reproductive health and make informed decisions about family planning.
Contraception Options
Various contraceptive methods, such as hormonal pills, patches, intrauterine devices (IUDs), and condoms, are effective in preventing pregnancy. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best option based on individual needs and preferences.
Hormonal birth control methods work by altering hormone levels in the body to prevent ovulation and thicken cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg. On the other hand, barrier methods like condoms create a physical barrier to prevent sperm from reaching the egg, reducing the risk of pregnancy.
The Importance of Regular Gynecological Check-ups
Regular gynecological check-ups are crucial for maintaining reproductive health. Through routine examinations, healthcare providers can assess fertility, address concerns, and provide guidance on contraception methods.
During gynecological check-ups, healthcare providers may perform pelvic exams, Pap smears, and screenings for sexually transmitted infections (STIs). These screenings are essential for early detection of any reproductive health issues and can help individuals take proactive steps to maintain their well-being.
Conclusion
While the likelihood of getting pregnant if you have unprotected sex during menstruation is generally lower, it is not impossible. Understanding the menstrual cycle, the timing of ovulation, and individual fertility factors is essential for making informed decisions about pregnancy prevention. By using reliable contraception methods and seeking regular medical care, individuals can effectively manage their reproductive health.