Discover the comprehensive guide to the benefits of Pregnyl for males.
The Benefits of Pregnyl for Males: A Comprehensive Guide
Pregnyl is a medication that has gained attention for its various benefits for males. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore its significant advantages and shed light on its composition, functioning, and potential side effects. Furthermore, we will provide essential information on how to use it safely and effectively for optimum results.
Understanding Pregnyl: What is it?
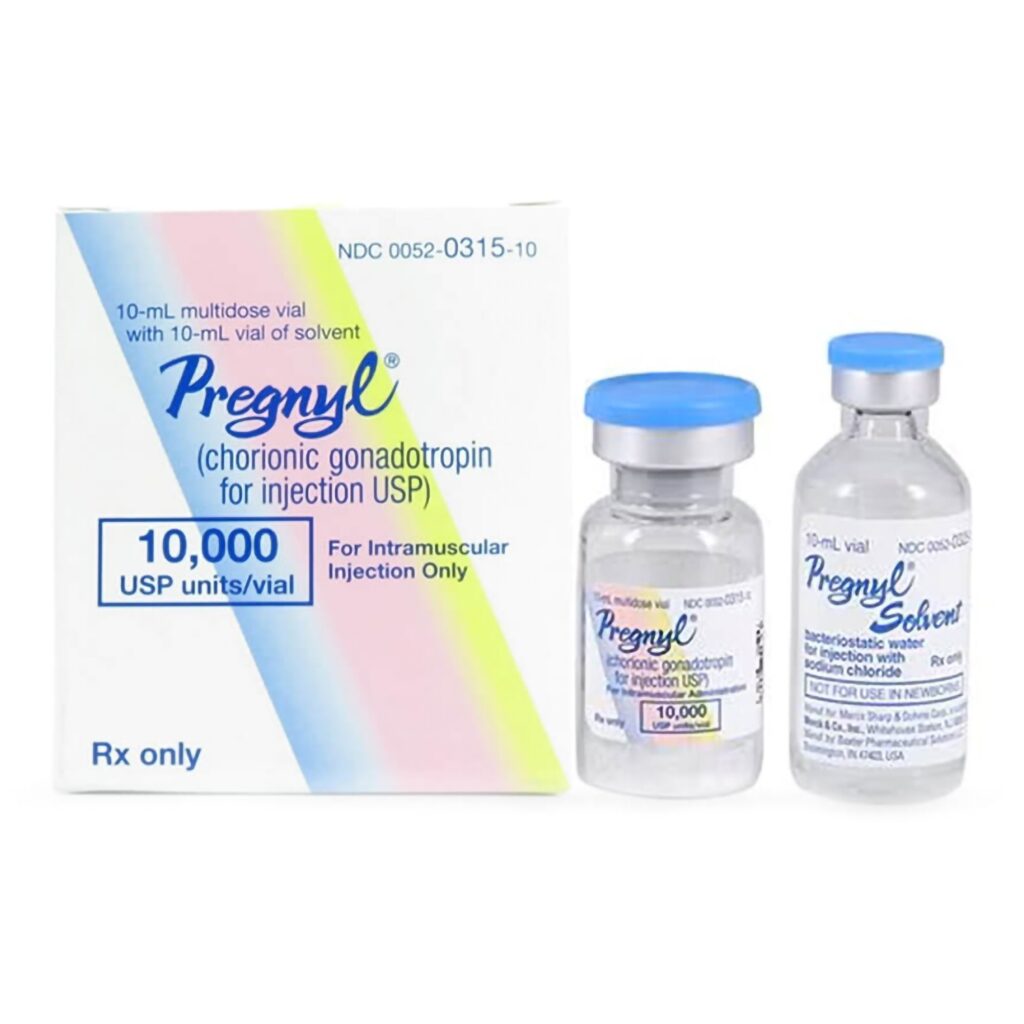
Pregnyl is a brand name for human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone naturally produced during pregnancy. While its primary role is to support the development of the embryo and placenta, Human Chorionic Gonadotropin has proven to offer significant benefits for males as well. Let’s delve deeper into its composition and functioning.
The Composition of Pregnyl
Pregnyl consists of purified hCG extracted from the urine of pregnant women. The resulting substance is then processed into a sterile powder form for administration. This composition ensures the potency and effectiveness of Pregnyl when used in male health scenarios.
Moreover, the extraction process of hCG for Pregnyl involves stringent purification techniques to guarantee the highest quality and purity of the hormone. This attention to detail in the manufacturing process underscores the commitment to producing a reliable and safe product for medical use.
How Pregnyl Works in the Body
When administered, Human Chorionic Gonadotropin mimics the activity of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the body. LH plays a vital role in stimulating the production of testosterone in males. By acting as a substitute for LH, Human Chorionic Gonadotropin triggers the production of testosterone and supports its maintenance at optimal levels.
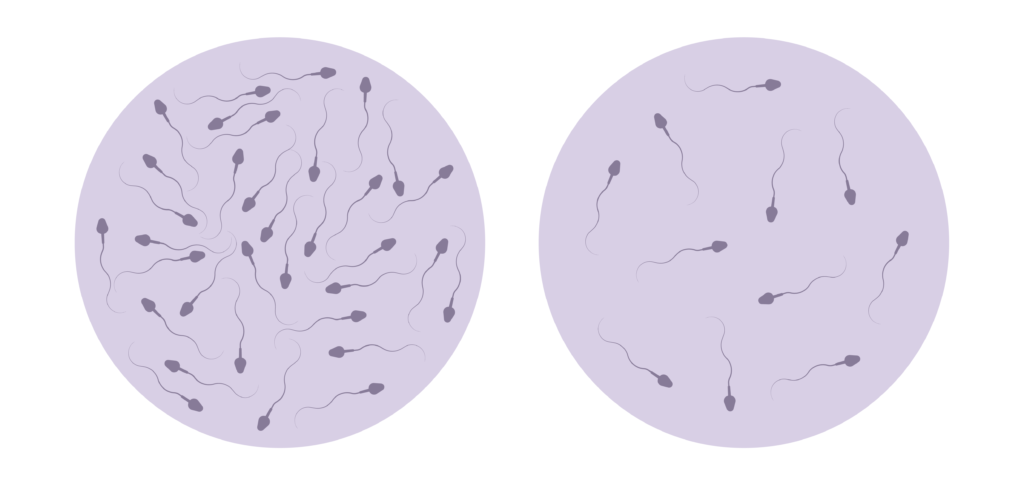
Furthermore, the mechanism of action of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin extends beyond testosterone regulation. Studies have shown that Human Chorionic Gonadotropin can also have a positive impact on other aspects of male reproductive health, such as improving sperm quality and motility. This multifaceted approach highlights the versatility of hCG in addressing various male fertility issues.
Additionally, Human Chorionic Gonadotropin can encourage the production and release of sperm, supporting male fertility and reproductive health. Let’s explore these aspects in more detail.
The Role of Pregnyl in Male Health
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin has shown promising potential when it comes to maintaining testosterone levels and positively impacting male health. Understanding the connection between hCG and testosterone levels is key to grasping its overall benefits.
hCG is commonly used in the medical field to address various health issues in males. Its ability to influence testosterone levels has garnered significant attention due to the hormone’s crucial role in male well-being.
Pregnyl and Testosterone Levels
Testosterone is a vital hormone for males, responsible for various aspects of their health, including muscle growth, energy levels, and sexual function. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin plays a crucial role in stimulating the production of testosterone, ensuring its normal levels are maintained within the body.
By using hCG, individuals with low testosterone levels may experience an increase in energy and vigor, improved mood, and enhanced sexual performance.
Furthermore, hCG’s impact extends beyond testosterone regulation. The hormone hCG, not only aids in testosterone production but also contributes to overall reproductive health in males.
Pregnyl’s Impact on Fertility
hCG can also be beneficial for males experiencing fertility issues. The hormone hCG, found in Pregnyl, can stimulate the production and release of sperm, enhancing male fertility. This factor makes hCG a valuable tool for couples struggling to conceive.
Moreover, hCG is sometimes prescribed in combination with other fertility treatments to optimize the chances of successful conception.
As research continues to explore the multifaceted benefits of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin in male health, its role in enhancing testosterone levels and fertility remains a topic of interest and potential breakthroughs in medical treatment.
The Benefits of Pregnyl for Males
Now that we have delved into the role of hCG in male health, let’s explore its specific benefits and the positive impact it can have on various aspects of life.
Understanding the multifaceted advantages of hCG is essential in comprehending its potential impact on male well-being. Beyond its primary functions, hCG has been found to play a crucial role in enhancing overall vitality and quality of life.
Enhancing Athletic Performance

For athletes and fitness enthusiasts, hCG has gained attention for its potential to boost performance. By maintaining optimal testosterone levels, hCG can support muscle growth, increased endurance, and improved recovery after intense workouts.
Moreover, the impact of hCG on athletic performance extends beyond physical attributes. It can also enhance mental focus and drive, enabling individuals to push their limits and achieve peak performance levels.
However, it is crucial to note that the use of hCG for athletic purposes must align with relevant sporting regulations and medical guidance.
Boosting Fertility and Reproductive Health
As previously mentioned, hCG offers a significant advantage to individuals facing fertility challenges. By stimulating sperm production and release, hCG increases the chances of successful conception. This benefit can bring hope to couples striving to start or expand their family.
Furthermore, the positive impact of hCG on reproductive health goes beyond fertility. It can also improve overall reproductive function, leading to enhanced sexual health and well-being.
Pregnyl and Weight Loss
Studies have suggested that hCG can contribute to weight loss when used in conjunction with a low-calorie diet. By maintaining testosterone levels, hCG helps preserve muscle mass during calorie restriction, preventing the loss of lean tissue.
Additionally, adequate testosterone levels can support metabolism, making it easier to achieve weight loss goals. This dual effect of preserving muscle mass and boosting metabolism highlights the potential of hCG in promoting sustainable and effective weight management strategies.
The Potential Side Effects of Pregnyl
While hCG offers various benefits, it is essential to be aware of the potential side effects associated with its use. Being informed allows individuals to make well-rounded decisions regarding their health.
Pregnyl, a medication commonly used in fertility treatments, contains human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) hormone. This hormone plays a crucial role in the development of eggs in women and sperm in men, making it a vital component in certain fertility procedures.
Common Side Effects
Some common side effects of hCG may include headache, fatigue, irritability, and tenderness at the injection site. These side effects are generally mild and temporary, subsiding on their own over time.
It is important to note that individual responses to hCG can vary, and not everyone will experience these common side effects. Factors such as dosage, frequency of use, and personal health conditions can influence the likelihood and severity of these symptoms.
However, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional if any side effects persist or become concerning.
Serious Side Effects
Although rare, hCG can potentially cause more serious side effects in some individuals. These may include severe allergic reactions, blood clots, and an increase in certain hormone levels. It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if any unusual symptoms occur.
Patients undergoing fertility treatments with hCG should be closely monitored by their healthcare providers to ensure early detection of any serious side effects. Regular check-ups and open communication about any changes or discomfort experienced during treatment can help mitigate risks and ensure the best possible outcomes.
How to Use Pregnyl Safely
When using hCG, it is essential to follow the recommended guidelines to ensure safety and maximize benefits. Let’s explore crucial factors to consider when using hCG.
First and foremost, let’s delve into the dosage and administration of hCG. This medication is typically administered via injection into a muscle, either subcutaneously or intramuscularly. The dosage and frequency of administration vary depending on the specific medical condition being treated. It is important to note that the dosage should be strictly adhered to as prescribed by your healthcare professional. Seeking guidance from a healthcare professional regarding the administration process is also highly recommended to ensure accurate and safe usage.
Now, let’s discuss some precautions and contraindications associated with hCG. While hCG offers significant benefits, it is not suitable for everyone. Individuals with a history of hormone-related cancers, allergic reactions to hCG, or severe kidney disease should avoid using hCG. It is crucial to inform healthcare professionals about any existing medical conditions or medications before beginning hCG treatment to ensure its safe use. This will allow them to assess whether hCG is the right choice for you and to provide appropriate guidance throughout your treatment journey.
Expanding on the topic of safety, it is important to be aware of potential side effects that may occur while using hCG. These side effects can include headache, irritability, restlessness, fatigue, and swelling or pain at the injection site. It is crucial to monitor your body’s response to the medication and report any unusual or severe symptoms to your healthcare professional promptly. They will be able to provide you with the necessary guidance and support to manage any potential side effects effectively.
In conclusion, Pregnyl holds several benefits for males, including the maintenance of testosterone levels, support for fertility, enhanced athletic performance, and potential weight loss or weight gain assistance. However, it is crucial to be aware of potential side effects and to use hCG safely by following proper administration guidelines and seeking appropriate medical advice. With its various advantages, hCG can contribute positively to male health and overall well-being.