Discover how HCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) can offer a range of impressive benefits for males, from increased testosterone levels to enhanced fertility and weight management.
The Impressive Benefits of HCG for Males
HCG, also known as Human Chorionic Gonadotropin, is a hormone that plays a crucial role in the male body. It offers several impressive benefits for men, ranging from enhancing testosterone levels to improving fertility and even promoting weight loss. In addition to these physical benefits, HCG can also provide positive psychological effects, such as mood enhancement and a boost in self-esteem. However, it is essential to understand the safety and potential side effects of HCG use in males. This article will delve into the various advantages of HCG for men, shedding light on its functions and how it can be utilized safely for optimal results.
Understanding HCG and Its Role in the Male Body
HCG is a hormone produced by the placenta during pregnancy. However, it is also present in small amounts in the male body. Its primary function is to stimulate the production of testosterone in the testicles. Testosterone is a vital hormone for male health, responsible for maintaining muscle mass, regulating libido, and promoting energy levels.
Despite being naturally produced, some males may have lower levels of HCG or testosterone. In such cases, HCG supplementation can help restore hormone balance and provide several health benefits.
What is HCG?
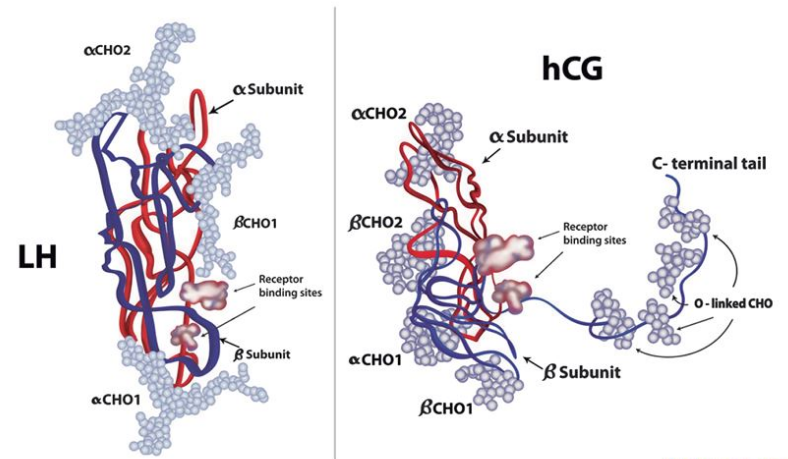
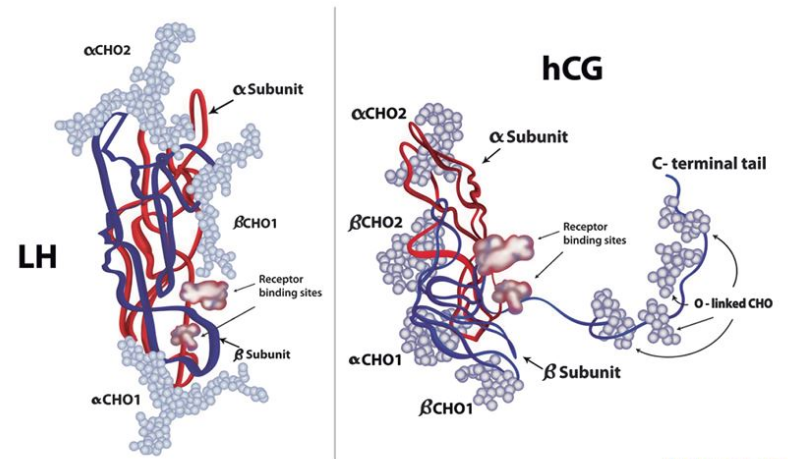
HCG is a glycoprotein hormone primarily produced during pregnancy. It is composed of an alpha and beta subunit that work together to perform various functions in the body.
When used medically in males, HCG is typically administered via injections. These injections help stimulate the testicles’ Leydig cells, which are responsible for testosterone production.
Additionally, HCG has been utilized in fertility treatments for men. By mimicking the action of luteinizing hormone (LH), HCG can help in the production and maturation of sperm, aiding in male fertility.
The Function of HCG in Males
For males, HCG serves as a bridge between the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and the testes. It stimulates the Leydig cells, which then produce testosterone. This process is crucial for maintaining proper hormone levels in the male body.
Moreover, HCG can prevent the testicles from shrinking during testosterone replacement therapy. It stimulates testicular function and preserves fertility.
Another important aspect of HCG in males is its role in weight loss and muscle maintenance. Some studies suggest that HCG injections, when combined with a low-calorie diet, can help preserve lean muscle mass while promoting fat loss. This has led to the use of HCG in certain weight loss programs, although its effectiveness for this purpose is still a topic of debate among experts.
The Health Benefits of HCG for Males
HCG offers several impressive health benefits for men, ranging from enhancing testosterone levels to promoting weight loss and improving fertility.
Enhancing Testosterone Levels
One of the primary benefits of HCG for males is its ability to enhance testosterone levels. By stimulating the Leydig cells in the testes, HCG promotes the production of testosterone. This can lead to increased energy levels, improved muscle mass, and a heightened sense of well-being.
Additionally, optimal testosterone levels contribute to better sexual health and libido. They play a crucial role in maintaining overall vitality and masculine characteristics.
Testosterone is not only important for physical health but also for mental well-being. It has been linked to improved mood, cognitive function, and even reduced risk of depression.
Improving Fertility
HCG is commonly used in fertility treatments for males. It helps stimulate the testes and ensures adequate production of sperm. By boosting sperm count and quality, HCG increases the chances of successful conception.
For men struggling with infertility, HCG can be an effective option to restore reproductive health and improve their chances of becoming fathers.
Furthermore, HCG has been found to have a positive impact on sperm motility, which refers to the ability of sperm to move effectively towards the egg. This is crucial for successful fertilization and pregnancy.
Weight Loss and Metabolism Boost
HCG has also gained popularity for its potential to aid in weight loss. It works by stimulating the hypothalamus, which can help suppress appetite and increase metabolism.
When combined with a low-calorie diet, HCG has been shown to promote fat loss while preserving lean muscle mass. This can lead to sustainable weight loss and improved body composition.
Moreover, HCG has been found to have a positive impact on insulin sensitivity. This means that it can help regulate blood sugar levels and potentially reduce the risk of developing conditions such as type 2 diabetes.
It is important to note that while HCG may aid in weight loss, it should always be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure safety and effectiveness.
The Psychological Benefits of HCG
In addition to its physical benefits, HCG can provide notable psychological effects for men.
Understanding the psychological impact of HCG treatment is crucial for a comprehensive approach to men’s health. Beyond the physical changes, the mental well-being of individuals undergoing HCG therapy is a significant aspect that should not be overlooked.
Mood Enhancement
Optimal hormone levels, including testosterone, play a vital role in mood regulation. By enhancing testosterone production, HCG can improve mood and reduce the risk of mood disorders such as depression.
Men who struggle with mood swings or feelings of irritability may find relief through HCG therapy. The stabilization of hormone levels can lead to a more balanced emotional state, allowing individuals to approach daily challenges with a greater sense of calm and positivity.
Many men report feeling more positive, energetic, and emotionally stable after undergoing HCG treatment.
Boosting Self-Esteem
Low testosterone levels can negatively impact self-esteem and confidence. By restoring hormone balance and enhancing testosterone levels, HCG can boost self-esteem and improve overall well-being.
Enhanced self-esteem is not just a superficial benefit of HCG therapy; it can have profound effects on various aspects of a man’s life. With increased confidence, individuals may find themselves more assertive in their personal and professional relationships, leading to greater success and fulfillment.
Men who have undergone HCG treatment often experience increased self-confidence and a more positive outlook on life.
The Safety and Side Effects of HCG Use in Males
While HCG offers significant benefits, it is essential to be aware of its safety and potential side effects.
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is a hormone commonly used in males to treat various medical conditions such as hypogonadism and infertility. However, like any medical treatment, HCG use in males comes with potential risks that should not be overlooked. Some individuals may experience allergic reactions, swelling, or pain at the injection site. These side effects are usually mild and temporary but should be reported to a healthcare professional if they persist or worsen. It is crucial to consult a healthcare provider before starting any HCG regimen to ensure it is safe and appropriate for individual needs.
Understanding the Risks
Additionally, there have been concerns raised about the potential long-term effects of HCG use in males, particularly in relation to fertility and hormone balance. While short-term use of HCG under medical supervision is generally considered safe, more research is needed to fully understand the impact of prolonged or excessive HCG use on male health.
It is important to note that HCG should only be used under the supervision of a medical professional and at the appropriate dosage to minimize the risk of adverse effects. Any misuse or overuse of HCG can lead to serious health complications and should be avoided.
How to Use HCG Safely
To use HCG safely, it is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional who has experience in hormone therapy. They will evaluate the individual’s hormone levels, overall health, and determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment based on specific needs and goals.
Regular monitoring of hormone levels, as well as follow-up visits with the healthcare provider, will help ensure the safe and effective use of HCG. It is important for individuals using HCG to communicate openly with their healthcare provider about any concerns or changes in their health status to optimize the benefits of treatment and minimize potential risks.
The Process of HCG Treatment
HCG treatment typically involves several steps, including consultation, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up.
Embarking on HCG treatment is a journey that begins with a crucial step – the initial consultation and diagnosis. This phase is pivotal as it sets the foundation for the entire treatment process. During the consultation, the healthcare provider delves into the individual’s medical history, symptoms, and potential hormonal imbalances. This comprehensive evaluation helps in determining the root cause of the issues at hand.
Consultation and Diagnosis
During the consultation, the healthcare provider will evaluate the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and potential hormonal imbalances. They may request blood tests to assess hormone levels accurately.
Following the consultation, the diagnosis phase commences. Through meticulous analysis and, if necessary, blood tests, the healthcare provider pinpoints the specific hormonal imbalances that may be causing distress. This diagnostic stage is critical in ensuring that the subsequent treatment plan is tailored to address the individual’s unique needs.
Based on the diagnosis, the healthcare provider will determine if HCG treatment is necessary and develop an individualized treatment plan.
Treatment and Follow-up
If HCG treatment is deemed appropriate, the healthcare provider will guide the individual through the treatment process. This typically involves self-administered injections of HCG at regular intervals.
Embarking on the treatment phase marks a new chapter in the individual’s journey towards hormonal balance and well-being. The administration of HCG through self-injections, under the guidance of the healthcare provider, is a key aspect of this phase. These injections are meticulously timed and dosed to optimize the effectiveness of the treatment.
Regular follow-up visits will allow the healthcare provider to monitor progress, adjust the dosage if needed, and ensure the treatment is delivering the desired benefits.
Continual monitoring and follow-up appointments play a pivotal role in the success of HCG treatment. These visits serve as checkpoints to assess the individual’s response to the treatment, make any necessary adjustments to the dosage or frequency of injections, and address any concerns or questions that may arise. The healthcare provider’s guidance and support throughout this process are instrumental in ensuring a smooth and effective HCG treatment journey.
Conclusion
HCG offers impressive benefits for males, ranging from enhancing testosterone levels to improving fertility and promoting weight loss. Additionally, it can provide psychological benefits, such as mood enhancement and a boost in self-esteem. However, it is crucial to use HCG safely and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Understanding the risks and following the recommended treatment process will help maximize the benefits while minimizing potential side effects. If you believe you could benefit from HCG treatment, consult a qualified healthcare professional to discuss your options and determine the most suitable approach for your unique needs.