Learn about the fertile window and ovulation cycle to understand how many days after your period you can get pregnant.
How Many Days After Your Period Can You Get Pregnant?
Many women may wonder how many days after their period they can get pregnant. Understanding the menstrual cycle and the various phases it entails can shed light on this question. Additionally, it is important to explore the concept of the fertility window, the role of ovulation in pregnancy, and the probability of getting pregnant after a period. By dispelling common myths and misconceptions, this article aims to provide accurate and helpful information for those seeking to conceive or avoid pregnancy.
Understanding the Menstrual Cycle
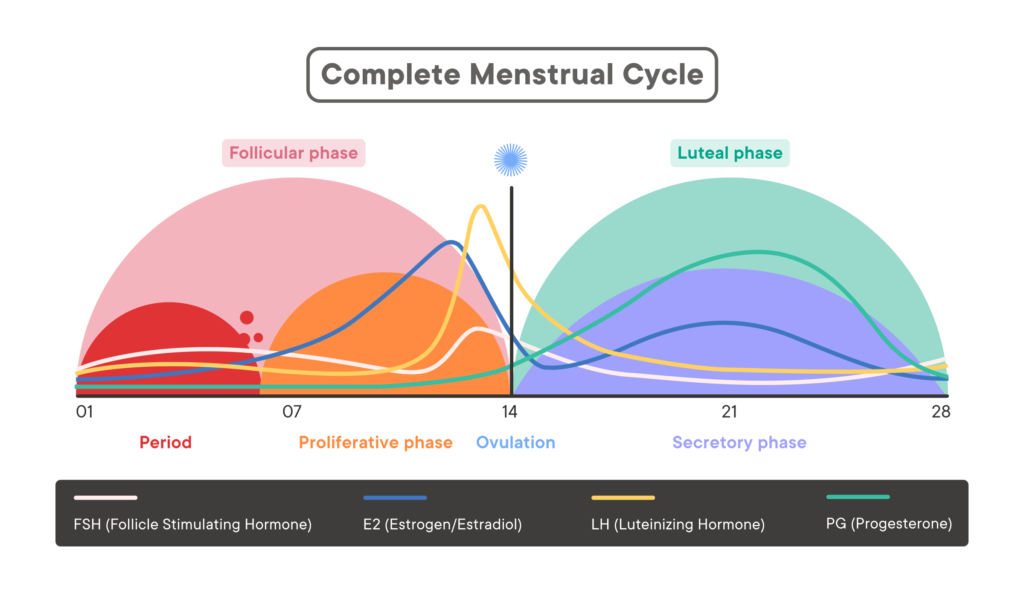
The Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle, a complex and intricate process, consists of several phases, each with its own unique characteristics. The first phase is the menstrual phase, marked by the shedding of the uterine lining and the start of a new cycle. This phase is crucial as it signifies the body’s readiness for a potential pregnancy. Following the menstrual phase is the follicular phase, a time when the body gears up for ovulation by stimulating the ovaries to release a mature egg. This phase is characterized by the growth of follicles in the ovaries, each containing an egg. The ovulation phase comes next, wherein a mature egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, awaiting fertilization by sperm. Finally, the luteal phase takes place, during which the uterus prepares for possible implantation of a fertilized egg by thickening its lining.
Each phase of the menstrual cycle is intricately timed and orchestrated by a delicate interplay of hormones and physiological changes within the body. Understanding these phases can provide valuable insights into reproductive health and fertility.
Hormonal Changes Throughout the Cycle
Throughout the menstrual cycle, hormone levels fluctuate, playing a crucial role in fertility and overall reproductive health. The levels of estrogen and progesterone, two key hormones, rise and fall in a carefully coordinated dance, influencing the growth and shedding of the uterine lining, as well as triggering ovulation. Estrogen, often referred to as the “female hormone,” is responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics and the regulation of the menstrual cycle. Progesterone, on the other hand, is known as the “pregnancy hormone” as it helps prepare the uterus for a potential pregnancy and supports early gestation.
By understanding these hormonal changes and their impact on the body, individuals can gain a deeper insight into their reproductive health and fertility. Monitoring these fluctuations can also aid in pinpointing the fertile window, the period during which conception is most likely to occur, offering valuable information for those trying to conceive or avoid pregnancy.
The Fertility Window: When Can You Get Pregnant?
Understanding your fertility window is crucial for those trying to conceive. The fertility window typically spans a few days in the middle of the menstrual cycle when the chances of getting pregnant are highest. This window is centered around ovulation, the process where an egg is released from the ovary and is available for fertilization by sperm. Identifying your personal fertility window can greatly increase the likelihood of successful conception.
To pinpoint your fertility window accurately, it is recommended to track your menstrual cycle diligently. This can be done using a traditional calendar or a mobile app specifically designed for fertility tracking. Ovulation predictor kits are also valuable tools that can help predict when the day of ovulation is likely to occur. Additionally, monitoring changes in cervical mucus consistency and basal body temperature can provide further insights into your body’s ovulation patterns.
Factors Affecting the Fertility Window
Several factors play a role in determining the duration and timing of the fertility window. The length and regularity of your menstrual cycle are key factors to consider, as they directly impact when ovulation is likely to occur. The lifespan of sperm and the egg also influence the fertility window, as sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for several days while the egg is viable for fertilization for a shorter period.

Individual variations in menstrual cycle length and ovulation patterns should not be overlooked when calculating the fertility window. While the average fertility window is often cited as occurring around day 14 of a 28-day cycle, it is essential to recognize that cycles can vary significantly among individuals. Ovulation may occur earlier or later in the cycle, making it crucial to pay close attention to your body’s unique fertility signs and signals.
The Role of Ovulation in Pregnancy
How Ovulation Works
Ovulation is the release of a mature egg from the ovary into the fallopian tube. This is a critical event in the menstrual cycle as it offers the opportunity for fertilization. Once released, the egg is viable for about 12 to 24 hours, requiring fertilization by sperm during this timeframe in order to result in pregnancy.
During ovulation, the egg is swept into the fallopian tube by tiny hair-like projections called cilia. The journey through the fallopian tube can take several days, during which the egg may encounter sperm for fertilization. If fertilization occurs, the resulting embryo will travel down the fallopian tube and implant in the uterus, leading to pregnancy.
Detecting Ovulation: Signs and Symptoms
While the exact timing of ovulation can vary, your body may provide signs and symptoms indicating that ovulation is approaching. These can include changes in basal body temperature, changes in cervical mucus consistency, and mild pelvic pain or discomfort. Familiarizing yourself with these signs can help you identify your most fertile days and increase the likelihood of conception.
Another common sign of ovulation is an increase in libido. Some individuals may experience heightened sexual desire during ovulation, which can be attributed to hormonal changes in the body. This surge in libido is nature’s way of encouraging procreation during the most fertile phase of the menstrual cycle.
The Probability of Getting Pregnant After Your Period
Day-by-Day Breakdown of Pregnancy Chances
While the odds of conceiving are generally lower during the earlier days of the menstrual cycle, it is essential to remember that sperm can survive in the reproductive tract for several days. Therefore, pregnancy can still occur if intercourse or unprotected sex takes place shortly after your menstrual period ends. As the menstrual cycle progresses, the chances of getting pregnant gradually increase, particularly during the fertile window.
During the fertile window, which typically occurs around the middle of the menstrual cycle, an egg is released from the ovary and is available for fertilization for about 12-24 hours. This is the prime time for conception to take place, as sperm can live in the female reproductive system for up to 5 days, eagerly awaiting the release of the egg. Understanding your menstrual cycle and tracking ovulation can be helpful in identifying the most fertile days for conception.
How Age and Health Impact Pregnancy Probability
Age and overall health can influence the probability of getting pregnant after a period. As women age, the quality and quantity of their eggs decline, making conception more challenging. Additionally, underlying health conditions, such as hormonal imbalances or reproductive disorders, can affect fertility. It is advisable to consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your fertility or need guidance on optimizing your chances of conception.
Factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor diet can also impact fertility. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can improve reproductive health and increase the chances of conception. In some cases, medical interventions such as fertility treatments may be necessary to overcome obstacles to conception. Seeking advice from a fertility specialist can provide personalized recommendations based on individual circumstances.
Myths and Misconceptions About Pregnancy and Menstruation
Debunking Common Myths
There are various myths surrounding pregnancy and menstruation that can lead to confusion and misinformation. One common misconception is that pregnancy cannot occur during menstruation. While it is less likely, it is not impossible, especially if the menstrual cycle is shorter than average or if ovulation occurs shortly after the period ends. It is crucial to have accurate knowledge about the reproductive process to make informed decisions.
Another prevalent myth is that exercising during menstruation is harmful. In reality, moderate exercise during this time can help alleviate menstrual cramps and improve mood due to the release of endorphins. Staying active can also promote overall well-being and may even help regulate menstrual cycles in some individuals.
Understanding the Facts
Understanding the intricacies of the menstrual cycle, the fertility window, and ovulation can empower individuals to make informed choices about their reproductive health. By dispelling myths and providing accurate information, this article aims to promote awareness and help individuals navigate their unique fertility journeys.
Furthermore, it is essential to address the myth that period blood is unclean or impure. Menstrual blood is a natural bodily function and is not dirty or harmful. In many cultures, menstruation is viewed as a sacred and powerful process, symbolizing fertility and the potential for new life. By challenging these misconceptions, we can foster a more positive and accepting attitude towards menstruation.