Discover the impact of HCG hormone on men’s health in this insightful article.
The HCG hormone, also known as human chorionic gonadotropin, plays a crucial role in men’s health. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of this hormone and its impact on male reproductive function, testosterone levels, and overall well-being. Understanding the HCG hormone is key to comprehending its potential benefits and risks in men’s health.
Understanding the HCG Hormone
The HCG hormone is a glycoprotein that is naturally produced in both men and women. It is primarily associated with pregnancy in women, as it is produced by the placenta to support fetal development. However, HCG also has essential functions in the male body, particularly concerning reproductive health and hormone regulation.
What is the HCG Hormone?
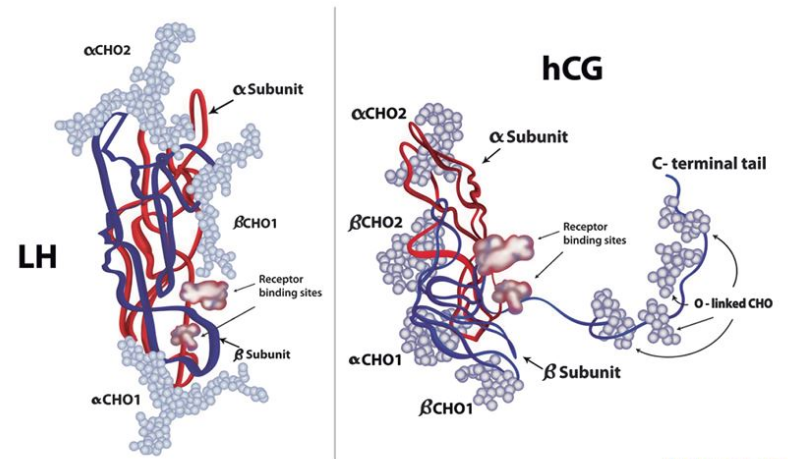
The HCG hormone is composed of two subunits: alpha and beta. The beta subunit is specific to HCG and is used to detect its presence in blood and urine tests. Higher levels of HCG are typically found in pregnant women, but men also produce smaller amounts of this hormone in their bodies.
The Production and Function of HCG Hormone
In men, HCG is produced by the cells in the pituitary gland and the placenta during fetal development. The primary function of HCG in male physiology is regulating the production of other hormones, such as testosterone. It also plays a role in supporting sperm production and fertility.
Furthermore, beyond its role in reproduction, HCG has gained popularity in weight loss treatments. Some weight loss clinics offer HCG injections along with a very low-calorie diet plan, claiming that HCG can help suppress appetite and promote fat loss. However, the effectiveness of HCG for weight loss is a topic of debate among healthcare professionals, with some studies suggesting that any weight loss observed is likely due to the restrictive diet rather than the hormone itself.
Research is ongoing to explore the potential therapeutic uses of HCG beyond its traditional roles in fertility and pregnancy. Scientists are investigating its impact on conditions such as obesity, hypogonadism, and even certain types of cancer. By understanding the multifaceted functions of the HCG hormone, medical professionals aim to uncover new treatment avenues and improve patient outcomes in various health conditions.
HCG Hormone and Male Fertility
Male fertility is greatly influenced by the levels of HCG in the body. The impact of HCG on sperm production and fertility has been the subject of extensive research. Understanding how HCG affects sperm production can provide insights into potential treatments for male infertility.
When delving deeper into the role of HCG in male fertility, it is important to highlight the intricate relationship between HCG and the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis. HCG mimics the action of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the body, which plays a crucial role in stimulating testosterone production by the Leydig cells in the testes. This increase in testosterone levels is essential for the process of spermatogenesis, where sperm cells are produced and matured.
The Impact of HCG on Sperm Production
Studies have shown that HCG stimulates Leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone, which is essential for sperm production. Higher levels of testosterone, induced by HCG, can lead to increased sperm production and improved sperm quality. This makes HCG a potential treatment option for men with low sperm count or poor sperm motility.
Moreover, the effects of HCG on sperm production extend beyond just quantity and quality. Research has indicated that HCG may also play a role in enhancing the maturation process of sperm cells, leading to a higher percentage of motile and morphologically normal sperm. This comprehensive impact on various aspects of sperm health underscores the significance of HCG in male fertility.
HCG Treatment for Male Infertility
In cases of male infertility, where low testosterone levels or inadequate sperm production are identified, HCG can be used as a therapeutic option. HCG therapy aims to stimulate testosterone production, which, in turn, enhances sperm production and improves fertility. However, it is crucial to consult with a medical professional for proper evaluation and guidance before considering HCG treatment for male infertility.
It is important to note that while HCG shows promise as a treatment for male infertility, individual responses to therapy may vary. Factors such as the underlying cause of infertility, overall health status, and genetic predispositions can influence the effectiveness of HCG treatment. Therefore, personalized treatment plans tailored to each individual’s specific needs and circumstances are essential for optimizing the outcomes of HCG therapy in male fertility.
HCG Hormone and Testosterone Levels
Testosterone is a vital hormone in men’s health, contributing to muscle mass, bone density, libido, and overall well-being. The relationship between HCG and testosterone has garnered interest among researchers and healthcare professionals alike.
The Relationship Between HCG and Testosterone
HCG acts as a luteinizing hormone (LH) analogue, meaning it has similar effects on the body as LH. LH stimulates the Leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone. By mimicking LH, HCG can help maintain or elevate testosterone levels in men, making it potentially useful for addressing low testosterone or hormonal imbalances.
HCG as a Treatment for Low Testosterone
HCG therapy has been explored as an alternative treatment for low testosterone levels in men. By stimulating natural testosterone production, HCG can potentially restore hormonal balance and alleviate symptoms of low testosterone, such as fatigue, decreased libido, and mood changes. However, the use of HCG for testosterone replacement therapy should be carefully monitored by healthcare professionals.
It is important to note that while HCG can be beneficial in boosting testosterone levels, it is not without potential risks and side effects. Like any hormone therapy, HCG treatment may lead to unwanted outcomes if not administered correctly or if dosages are not carefully monitored. Some of the side effects associated with HCG therapy include acne, fluid retention, and breast tenderness.
Furthermore, the use of HCG for testosterone enhancement is a topic of ongoing research and debate within the medical community. Some experts argue that the long-term effects of HCG on testosterone production and overall health are not yet fully understood, emphasizing the need for more comprehensive studies to determine its efficacy and safety as a treatment for low testosterone.
The Side Effects and Risks of HCG Use in Men
Like any hormonal treatment, HCG use carries potential side effects and risks. Understanding these risks is essential for making informed decisions regarding the use of HCG in men’s health.
When delving into the realm of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) use in men, it is crucial to explore not only the immediate effects but also the potential long-term consequences. While HCG is commonly utilized for various health purposes, including fertility treatments and hormone regulation, its impact on male physiology can be multifaceted and nuanced.
Potential Side Effects of HCG
Common side effects of HCG include acne, mood swings, fluid retention, and injection site reactions. These side effects are generally mild and temporary, but it is important to consult with healthcare professionals if they become persistent or severe.
Moreover, it is imperative to recognize that individual responses to HCG can vary significantly. Factors such as dosage, frequency of administration, and underlying health conditions can influence the manifestation and severity of these side effects. Monitoring and adjusting HCG therapy under the guidance of a knowledgeable healthcare provider can help mitigate these potential challenges.
Long-Term Risks of HCG Use
Long-term use of HCG may have unknown risks and implications for overall health. The impact of prolonged HCG therapy on fertility, cardiovascular health, and prostate health requires further research and investigation.
As research continues to evolve in the field of male hormonal therapy, the exploration of HCG’s long-term risks remains a critical area of interest. Understanding the interplay between HCG supplementation and male reproductive health, cardiovascular function, and prostate function is essential for optimizing the safety and efficacy of HCG use in men.
The Future of HCG in Men’s Health
The potential applications of HCG in men’s health extend beyond fertility and testosterone regulation. Ongoing research and scientific advancements continue to shed light on new uses and benefits of the HCG hormone.
Ongoing Research into HCG and Men’s Health
Researchers are exploring the role of HCG in various conditions, such as hypogonadism, male contraception, and age-related hormone decline. As scientific knowledge and understanding of HCG expand, new treatment options and approaches may emerge.
One area of particular interest is the potential link between HCG and weight loss in men. Some studies suggest that HCG may play a role in promoting fat loss and preserving muscle mass when used in conjunction with a low-calorie diet. While more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind these effects, the findings open up new possibilities for utilizing HCG in men’s health beyond traditional applications.
Potential New Uses for HCG in Men’s Health Treatment
Studies have suggested potential applications of HCG in areas such as muscle growth and athletic performance enhancement. While these findings are preliminary, they highlight the ongoing exploration of HCG’s role and potential benefits in enhancing men’s health and well-being.
Furthermore, emerging research is investigating the role of HCG in addressing metabolic disorders and improving insulin sensitivity in men. The hormone’s influence on various metabolic pathways could offer new avenues for managing conditions like diabetes and obesity, providing a holistic approach to men’s health beyond conventional treatments.
In conclusion, the HCG hormone plays a vital role in men’s health, impacting fertility, testosterone levels, and overall well-being. Its ability to regulate hormone production and stimulate testosterone synthesis makes it a potential treatment option for male infertility and low testosterone. However, like any medical intervention, it is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals to fully understand the benefits, risks, and appropriate use of HCG in men’s health. Ongoing research into HCG and novel applications in men’s health treatment holds promise for the future.