Discover the potential link between fasting and ovulation in this informative article.
Can fasting help with ovulation?
Fasting has gained popularity as a potential strategy for various health benefits, including weight loss, improved metabolism, and better mental clarity. However, its impact on female fertility, specifically ovulation, is a topic that requires further exploration. In this article, we will delve into the basics of fasting, the science behind ovulation, the connection between fasting and ovulation, and the potential risks and benefits associated with fasting for ovulation.
Understanding the Basics of Fasting
Defining Fasting
Fasting is the practice of abstaining from consuming food and, in some cases, drinks with calories for a specific period. It has been an integral part of different cultural, religious, and spiritual traditions for centuries. The concept of fasting goes beyond just physical abstinence; it is often seen as a way to cleanse the body, focus the mind, and demonstrate discipline.

Many people also turn to fasting for its potential health benefits, such as weight loss, improved metabolic health, and increased longevity. Research has shown that fasting can trigger various cellular processes that promote overall well-being.
Different Types of Fasting
There are various fasting methods, each with its own set of guidelines. Some popular types include:
- Intermittent fasting: This involves alternating periods of fasting and eating. Common methods include the 16/8 method (fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window) and 5:2 method (eating normally for 5 days and significantly reducing calorie intake for 2 non-consecutive days). Intermittent fasting has gained popularity for its simplicity and flexibility, making it easier for people to incorporate into their lifestyles.
- Extended fasting: This refers to prolonged fasting periods, ranging from 24 hours to several days. Extended fasting is often used for specific health goals or as part of religious practices. While it can be challenging, proponents believe that extended fasting allows the body to enter a state of deeper healing and regeneration.
Additionally, there are other variations of fasting, such as water fasting, where only water is consumed for a set period, and juice fasting, which involves consuming only fruit and vegetable juices. Each type of fasting has its own unique effects on the body and requires careful consideration and planning to ensure safety and effectiveness.
The Science Behind Ovulation
The Ovulation Cycle Explained
Ovulation is a vital part of the menstrual cycle, which typically lasts about 28 days. It involves the release of a mature egg from the ovary, allowing it to travel through the fallopian tube for fertilization. Ovulation usually occurs around the middle of the cycle.
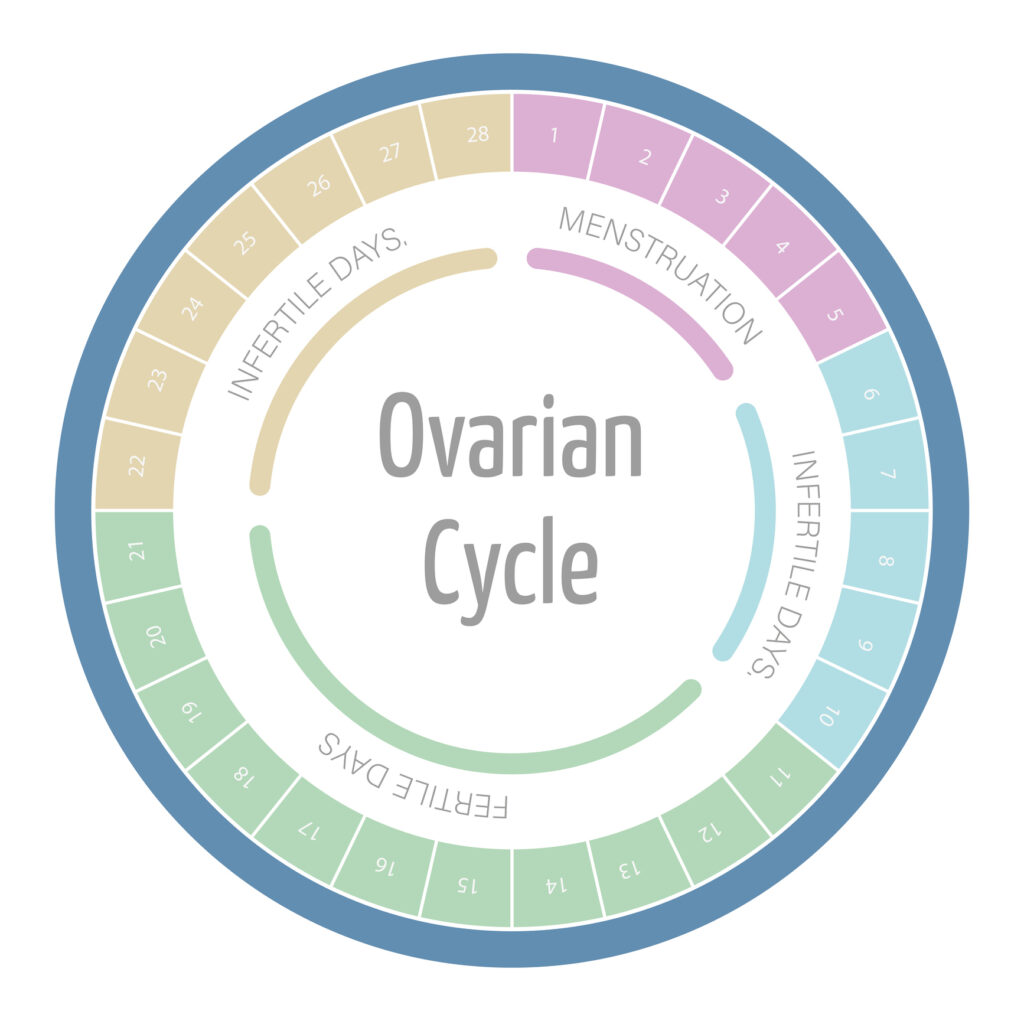
During ovulation, the egg is released from the dominant follicle in the ovary, which ruptures to let the egg out. The egg is then swept into the fallopian tube by tiny hair-like structures called cilia, where it awaits fertilization by sperm. If fertilization does not occur within 12-24 hours, the egg disintegrates and is absorbed by the body.
Factors Influencing Ovulation
Several factors influence ovulation, including hormonal balance, stress levels, body weight, and overall health. Hormonal imbalances, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or irregular menstrual cycles, can hinder ovulation.
Stress can also play a significant role in disrupting ovulation. When the body is under stress, it can affect the production of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which in turn can impact the delicate balance of reproductive hormones necessary for ovulation. Finding ways to manage stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or therapy can help support regular ovulation.
Fasting and its Impact on the Body
Fasting is a practice that has been around for centuries and is known to trigger numerous physiological changes in the body. As insulin levels decrease during a fast, the body switches to burning stored fat for energy. This metabolic shift not only aids in weight loss but also improves insulin sensitivity, which is beneficial for individuals with conditions like diabetes.
Moreover, during fasting, the body goes through a process called autophagy, where it cleans out damaged cells and regenerates new, healthy ones. This cellular repair mechanism is believed to have anti-aging effects and may help protect against various diseases.
Physiological Changes During Fasting
Fasting triggers numerous physiological changes in the body. As insulin levels decrease, the body switches to burning stored fat for energy. This metabolic shift may promote weight loss and improve insulin sensitivity.
Additionally, fasting can lead to a reduction in inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is linked to various health issues, including heart disease, cancer, and arthritis. By reducing inflammation through fasting, individuals may experience improved overall health and a lower risk of developing inflammatory conditions.
Fasting and Hormonal Balance
Fasting has been proposed as a potential method for optimizing hormonal balance. It may help regulate hormones such as insulin, growth hormone, and cortisol, which are all crucial for reproductive health.
Furthermore, fasting has been shown to have a positive impact on brain health. It can enhance brain function, promote clarity of thought, and even protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. The production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports the growth and maintenance of neurons, is increased during fasting, contributing to cognitive benefits.
Fasting and Ovulation: The Connection
How Fasting Might Affect Ovulation
Research investigating the direct impact of fasting on ovulation in women is limited. However, animal studies suggest that caloric restriction, a form of fasting, may impact female fertility by altering hormonal profiles and disrupting the delicate balance needed for ovulation.
Furthermore, fasting has been shown to affect the production of key reproductive hormones such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which play crucial roles in the ovulation process. Changes in the levels of these hormones due to fasting can potentially lead to irregular menstrual cycles and ovulatory dysfunction.
The Role of Insulin Resistance and Fasting
Insulin resistance, a condition in which cells become less responsive to insulin, has been linked to hormonal imbalances and difficulties with ovulation. Some studies suggest that intermittent fasting or calorie restriction may improve insulin sensitivity, potentially benefiting ovulation in women with insulin resistance.
Moreover, insulin resistance can contribute to anovulation, a condition where the ovaries do not release an egg during the menstrual cycle. By addressing insulin resistance through fasting, women may have a better chance of restoring normal ovulatory function and improving their fertility.
Potential Risks and Benefits of Fasting for Ovulation
Possible Health Benefits
While fasting for ovulation is still an area that requires more extensive research, there are potential health benefits associated with fasting. These include improved insulin sensitivity, weight management, and hormonal balance, which may indirectly support ovulatory function.
Furthermore, some studies suggest that intermittent fasting could help reduce inflammation in the body, which is crucial for reproductive health. By giving the digestive system a break during fasting periods, the body can focus on repair and rejuvenation processes, potentially benefiting overall fertility.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
It is essential to approach fasting with caution, especially for women trying to conceive. Extreme or prolonged fasting may lead to nutritional deficiencies, hormone imbalances, and disruptions in menstrual cycles, all of which could affect ovulation adversely.
In addition, fasting can increase stress levels in some individuals, triggering the release of cortisol, a hormone that, when elevated long-term, can interfere with reproductive hormones and ovulation. This underscores the importance of personalized approaches to fasting, taking into account individual health status and needs.
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before embarking on any fasting regimen, particularly if you have pre-existing health conditions or are planning to conceive.
In conclusion, the relationship between fasting and ovulation remains a subject of ongoing scientific investigation. While fasting may have potential benefits for overall health and hormonal balance, its direct impact on ovulation and fertility in women requires further research. It is always recommended to seek guidance from healthcare professionals to ensure personalized and appropriate advice. Remember, the journey to optimal reproductive health combines various factors, including nutrition, exercise, stress management, and a balanced approach to fasting, if chosen as part of your health journey.