Endometriosis & Pregnancy: Comprehensive Guide to Risks, Symptoms, and Management
Endometriosis is a prevalent gynecological condition that affects millions of women worldwide. It occurs when the endometrial tissue, which typically lines the uterus, starts growing outside the uterus. This abnormal growth can lead to severe pain, inflammation, and in some cases, fertility issues. This article delves into the complex relationship between endometriosis and pregnancy, exploring the symptoms, treatment options, and strategies to improve fertility for women living with endometriosis.
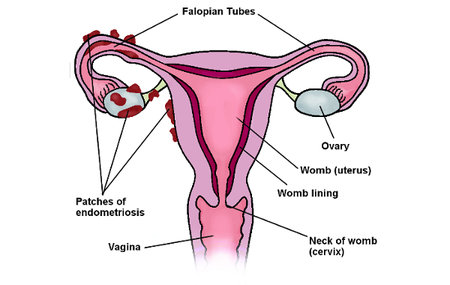
Symptoms and Diagnosis: Identifying Endometriosis in Women
The symptoms of endometriosis can vary significantly among women. Some common signs include:
- Painful periods (dysmenorrhea)
- Heavy bleeding during menstruation
- Pain during intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Lower back and pelvic pain
- Fatigue and gastrointestinal issues
Diagnosing endometriosis can be challenging, as its symptoms often overlap with other conditions. In most cases, doctors rely on a combination of physical examinations, medical history, and imaging tests such as ultrasounds or MRIs. However, the gold standard for endometriosis diagnosis remains laparoscopy. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows direct visualization of the endometrial lesions.
Endometriosis and Pregnancy: Exploring the Connection
Approximately 30-50% of women with endometriosis experience fertility issues. The connection between endometriosis and fertility is multifaceted, with several factors contributing to the problem:
- Inflammation and scarring: Endometriosis can cause inflammation and scarring in the pelvic region. This can interfere with the normal function of reproductive organs such as the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
- Altered hormonal environment: Hormonal imbalances related to endometriosis can affect the menstrual cycle and impair ovulation. This makes it difficult for women to conceive.
- Immune system dysfunction: Research suggests that endometriosis may be linked to immune system abnormalities. This could hinder the body’s ability to support a healthy pregnancy.
Effective Treatment Strategies to Get Pregnant with Endometriosis
To address fertility concerns in women with endometriosis, healthcare providers employ a range of treatments tailored to the individual’s specific needs:
- Medications:
Hormonal therapies, such as birth control pills, progestins, and gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, can help manage endometriosis symptoms. - Surgical interventions:
Laparoscopic surgery can remove endometrial lesions and scar tissue, potentially improving fertility by restoring normal pelvic anatomy and function. - Assisted reproductive technologies (ART):
In vitro fertilization (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI) are common ART methods that can help women with endometriosis.
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care for Pregnancy with Endometriosis
In addition to medical treatments, women with endometriosis can benefit from adopting certain lifestyle changes and self-care practices to support fertility:
- Maintain a healthy diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help manage inflammation and support overall reproductive health.
- Exercise regularly: Moderate physical activity can help regulate hormones, alleviate endometriosis symptoms, and improve fertility.
- Manage stress: Stress reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or mindfulness can help improve overall well-being and fertility.
Conclusion
Living with endometriosis can be challenging, particularly when it affects fertility. However, with the right support and treatment plan, many women with endometriosis can successfully achieve pregnancy and build the family they desire.
It is essential for women with endometriosis to work closely with their healthcare providers, including primary care physicians, gynecologists, and fertility specialists. This collaborative approach ensures that each patient receives comprehensive, personalized care tailored to their unique circumstances.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to improving fertility outcomes for women with endometriosis. If you suspect you have endometriosis don’t hesitate to discuss your concerns with your healthcare provider. They can help you develop an effective treatment plan, provide guidance on lifestyle changes, and explore assisted reproductive technologies if necessary.
In conclusion, the journey to parenthood for women with endometriosis may be challenging, but it is not impossible. By staying informed, working closely with your healthcare team, and adopting a proactive approach to managing your condition, you can improve your chances of achieving a healthy pregnancy and welcoming a new life into your family.
While we work diligently to provide the most accurate and up-to-date information available, it’s important to remember that every individual’s fertility journey is unique. The advice and content on this blog are intended for general informational purposes only and may not apply to your specific situation. Fertility-related concerns should always be addressed by a licensed healthcare provider. It is crucial to seek professional medical guidance to ensure that any treatments or recommendations align with your individual needs. Please consult with your doctor or a fertility specialist for a more personalized and thorough evaluation.